What is Supply Chain Strategy?
Supply Chain Strategy or Strategic Supply Chain Management is defined as: “ A strategy that defines how the supply chain works in order to meet the specific organizational business and strategic goals”. Supply Chain strategies focuses on the optimization of supply chain operations, that is improved efficienty, reduced supply chain costs, and increased customer sataisfaction, while making sure that it follows the industry standards. While developing a supply chain strategy, it must be assured that it aligns with the organization’s business goals and will result in long-term sustainability.
Role of Supply Chain Strategies in Organizational Success
Importance of Supply Chain Strategy
There’s a kind of magic in some words, “strategy” and “strategic” being key examples. Place “strategic” in front of the name of any business process and suddenly that process acquires an aura of great importance. Strategic objectives cry out to be achieved in a way that simple objectives do not. Strategic planning sounds considerably more sophisticated and powerful than plain old planning. There’s a reason those words have such power. Strategy, originally a military term, is how generals marshal all available resources in pursuit of victory. Strategy wins football games and chess matches—or loses them.
Evolving Supply Chain Strategies for Value Creation
It’s really the same in the business world. Each company has a business strategy that paints a broad picture of how they will compete in the marketplace. Since business strategy is like military strategy in that it requires the marshaling and organizing of all its resources, then it becomes clear that the business’s supply chain can be its most potent strategic resource. Designing and building the right supply chain, one that promotes the business strategies, may just be the most powerful way to gain an edge on the competition, to move faster, deliver more value, and be more flexible in the face of both steady change and surprises. The supply chain strategy is a complex and evolving means that organizations use to distinguish themselves in the competitive contest to create value for their customers and investors.
Aligning Supply Chain Strategies with Busiess Strategy
As illustrated in figure mentioned below, you can see how the direction of a firm or organization is predicated on its business strategy. Of course many organizations now also use mission and vision statements to give clarity to their purpose. If these strategies are not aligned, the direction and fit will be askew. All three strategies are linked and dependent.
Business Strategy VS Supply Chain Strategy
What is Business Strategy?
Business Strategy is a plan for choosing how to compete. Three generic business strategies are:
- Least cost.
- Differentiation.
- Focus.
Integrating Organizational and Supply Chain Strategy
The strategy of an enterprise identifies how a company will function in its environment. This supply chain strategy specifies how to satisfy customers, how to grow the business, how to compete in its environment, how to manage the organization and develop capabilities within the business, and how to achieve financial objectives.
Prior to discussing organizational and supply chain strategy in more detail, the first topic in the section addresses business strategy and competitive advantages. Competitive advantages are closely related to business strategy because they outline the advantages the organization should realize once it has decided how it will compete. Other concepts covered in this section include:
- Organizational and supply chain strategy.
- Prioritization options.
- Organizational capabilities.
- Alignment of capabilities and strategy.
- Resolving misalignment or gaps.
Understanding the Supply Chain Strategic Planning
1. Hybrid Supply Chain Strategic Planning Approach
Typically a business strategy among supply chain strategies will outline how to grow the business,
- How to distinguish the business from the competition and outperform them,
- How to achieve superior levels of financial and market performance, and
- How to create or maintain a sustainable competitive edge.
As per the definition provided previously, business strategies include least cost, differentiation, and focus. Least cost relates to a lower cost than the competition for an otherwise equivalent product or service. Differentiation relates to a product or service with more features, options, or supply chain operations model than the competition. Focus relates to whether the product or service is designed for a broad audience or a well-defined market segment or segments. There are many ways that these generic strategies can be combined or made into hybrids. For example, common business strategies that are generic to many industries and manufacturers include the following variations:
- Best cost—creates a hybrid, low-cost approach for providing a differentiated product or service.
- Low cost—focuses on delivering low-price and no-frills basics with prices that are hard to match.
- Broad differentiation—creates product and service attributes that appeal to many buyers looking for variety of goods.
- Focused differentiation—develops unique strategies for target market niches to meet unique buyer needs.
- Focused low cost – designed to meet well-defined buyer needs at a low cost.
Supply Chain Strategies for Achieving Low Cost Advantage
Competitive advantages mirror the strategies used to create them: A competitive advantage exists when an organization is able to provide the same benefits from a product or service at a lower cost than a competitor (low cost advantage), deliver supply chain benefits that exceed those of a competitor’s product or service (differentiation advantage), or create a product or service that is better suited to a given customer segment than what the competition can offer (focus advantage). The result of this competitive advantage is superior value creation for the organization and its customers. If this advantage is successfully implemented and marketed, it should result in improved profits and market share.
The following discussion is divided into two ways to create a focus advantage:
- Niche marketing Strategies.
- Responsiveness Strategies.
1. Niche Marketing Strategies for High-Net-Worth Customers
- Firms can choose to develop products and services for a mass market or for a relatively small slice of a larger market – a market niche. Some examples of niche market approaches include:
- Catering to high-net-worth customers with products such as luxury automobiles, yachts, large homes, or specialized services such as estate planning, personal training, or expensive cruises.
- Designing for a limited age group, such as children or senior citizens with special needs instead of serving a broader population.
- Providing products or services for residents of a particular geographic area, such as growing vegetables for a neighbourhood market rather than for packaging and shipping around the nation or world.
Niche marketing shares some characteristics with product service differentiation. In both cases, the product or service provided to customers has special features. Differentiation by quality, for example, can be the same thing as catering to high-net-worth customers. (Low-net-worth customers, or value shoppers, can also be niche.) Therefore, some supply chain strategies will work for both approaches. Collaboration to achieve distinctive design is one example. Depending upon the niche, sourcing may focus more on finding special expertise or high-quality materials rather than on low-cost labor.
2. Responsiveness: Speed VS Quality
Perhaps the most obvious example of responsiveness is the fast-food industry that grew up in the last half of the 20th century, led by McDonald’s. Diners at fine restaurants will happily wait half an hour for their specially cooked steak, but employees on short lunch breaks become impatient with even a few minutes in line as their sandwiches are prepared, using the logistics or supply chain strategy.
a. Example
In the early days of the Toyota Prius automobile – a highly differentiated car—buyers were known to wait for months for a new vehicle. (The same phenomenon occurred when the Volkswagen “Beetle” first came to the United States, where it was both highly differentiated and a low-cost option.) But businesspeople or diplomats on assignment expect a rental car or limousine to be ready immediately when they arrive at the airport. Manufacturers of clothing prosper or go bankrupt by their ability to bring the latest seasonal designs to market rapidly. Perishable products, such as raw food items, must be delivered rapidly, unlike preserved foods. Services may also compete on the basis of speed by cutting time spent waiting on the phone, standing in line, or processing paperwork.
b. Managing Overstocked Seasonal Items
Supply chains designed for responsiveness may rely on substantial supplies of safety stock to avoid outages. (Overstocked seasonal items typically go on sale at the end of the season.) They may also have multiple warehouses to place products nearer to users. Third-party logistics providers of rapid transportation, such as package delivery services, were developed to suit the needs of such supply chains.
How to Balance Multiple Supply Chain Strategies?
While some firms may focus primarily on one business strategy, others may pursue a mix of strategies. Note, however, that making one strategy the priority may make other strategies difficult to achieve. For example, providing high quality at the lowest price is a challenge. But not all the strategies are mutually exclusive. Product differentiation and niche marketing fit well together. Either responsiveness or low cost may be a key competitive factor that differentiates a firm from its market rivals.
Once an organization has decided on a business strategy, it uses these choices to drive the organizational strategy and eventually the supply chain strategy.
Organizational and Supply Chain Strategy, Prioritization, Capabilities, and Alignment
1. Aligning Supply Chain Strategy with Business Goals
Recall that the supply chain strategy of an enterprise identifies how a company will function in its environment. The strategy specifies how to satisfy customers, how to grow the business, how to compete in its environment, how to manage the organization and develop capabilities within the business, and how to achieve financial objectives.
Where do you start when building an organization’s strategy? As author and business consultant Stephen R. Covey says in The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People, “begin with the end in mind,” that is, think first about the goals of the supply chain strategy.
2. Cost Management through Effective Sourcing
Whatever strategy the corporation adopts to satisfy customers, grow, compete, organize itself, and make money, the supply chain has to operate in a manner that furthers those goals. To give a simple example, if customers are clamoring for deeply discounted prices on durable, high-volume goods with stable demand, a supply chain strategy that invests heavily in sourcing lower-cost materials in emerging markets would be on target for accomplishing that goal. Low-cost sourcing is probably the best option for this strategy because purchasing machines involves a high capital investment and lower labor expenses could help offset the investment costs. However, you might also look into investing in equipment, as the high investment is covered by lower labor costs and increased revenue. (It is possible for an organization to do both¬ invest in automation and move into a geographic area where labor costs are less. That decision would be based on volume, payback period, product life cycle, etc.).
3. Strategies for Synchronizing Organizational and Supply Chain Goals
Horizontal supply chains will contain a number of independent organizations, each with its own goals, processes, operations, technology, and strategy. So, when we refer to the necessity of aligning supply chain strategy with organizational strategy, we are referring to the strategies of a channel master or nucleus firm. Traditionally, that’s the manufacturer of a product—the company that sits right at the center of the chain (or network) with suppliers in tiers on one side and customers on the other.
4. Aligning Strategies Across the Supply Chain
However, if a supply chain has a dominant firm with a dominating supply chain strategy (one that is dictating its requirements to others), for example, a large retailer, then supplier and manufacturer strategies and goals must align with that retailer’s organizational and supply chain strategies. The suppliers of suppliers also have strategies to be brought into alignment. Finally, the strategies, once aligned, have to do two things: serve the end customers’ needs and be profitable for the chain as a whole and each company individually.
4 Types of Supply Chain Strategies
The following looks at four types of organizational strategy in detail:
- Customer focus and alignment,
- Forecast-driven enterprise,
- Demand-driven enterprise, and,
- Number of supply chains.
Strategy # 1: Supply Chain Strategies for Balancing Customer Needs
When it comes to supply chains, it’s what’s good for the customer that counts not what’s good for the nucleus company or even what seems to be good for the supply chain itself. Supply chain management needs to be focused on giving the final customer the right product at the right time and place for the right price. It isn’t necessarily about the most advanced product or service, nor is it always about the lowest price, the fastest time, or the most convenient place. It’s about the balance of quality, price, and availability (timing and place) that’s just right for the supply chain’s customer.
How does one determine what is the right amount of each of those factors? There isn’t a simple formula that will help the supply chain manager with this decision. But there are some basic premises that will help you get started in determining the appropriate balance:
- Serving the end-user customer is the primary driver of supply chain decisions.
- Organizations in the supply chain have to make a profit and stay in business to serve the customer.
a. Data-Driven Strategies for Supply Chain Management
Functional teams in the organization will provide their input and research on the optimal balance for the supply chain to meet customer needs. Design engineers – or, better yet, design teams from across the network—design products that are right for the end customer and can be sold profitably. Market research looks for the true, and not always obvious, needs in potential consumers that the supply chain can be engineered to satisfy profitably. Logistics supply chain strategy begins with data about customer demands for availability—of materials, components, service, or finished products, depending upon the customer—and then it looks for ways to move products in a cost-effective way with acceptable supply chain risk.
b. Complexity of Customer Relationships in Supply Chains
Decisions are not just about product features or price or speedy delivery. They are about the right features at the right price on the right schedule. DOS was not a great operating system; it was just the right operating system for the time and the market.
The term “customer” can be a complex concept in supplier relationship management because there are multiple customers with different stakes in the process. When we talk about customer focus, we mean the end user, the consumer of the product. But usually only the retailer actually sees the end user and has a direct relationship with that person or entity.
c. Meeting Customer Needs for Overall Success
Everyone else in the supply chain has a more immediate customer just downstream to our right in the supply chain diagram. If the supply chain is completely aligned in its focus on the end customer, then, at least in theory, serving the customer just to an organization’s downstream side would automatically serve the end user and also be in the supplying organization’s best interest as well as the interest of investors.
Moreover, within each supply chain partner there are internal “customers” whose needs also must be aligned with corporate and supply chain strategies. Each manager must understand his or her role in making the supply chain profitable, and staff, too, must be rewarded, motivated, and trained in alignment with the needs of the supply chain’s end customer.
d. Importance of Collaboration for Sustainable Supply Chain Management Strategy
Consider sustainable supply chain management. Successfully managing for sustainability requires a strategic mindset, involving numerous personnel and financial resources and a commitment from suppliers from first to lower tiers of the supply chain as well as consumers further up the supply chain. Departments must cooperate with other departments in their organization (e.g., purchasing and environmental or design departments) and with their counterparts at suppliers. This type of collaboration between supply chain partners necessitates breaking down cultural barriers and building a culture of trust to ensure that the focus is on end-to-end supply chain activities and not just discrete supply chain processes. Creating and managing a sustainable supply chain requires an organization to be informed, exercise leadership, and cooperate in supply chain operations with partners to achieve positive results on the triple bottom line.
Strategy # 2: Forecast-Driven Enterprises
A second supply chain strategy is the forecast-driven enterprise. Simply put, this strategy is one in which the nucleus firm, usually their manufacturer, utilizes a forecast, an estimate of future demand, as the basis of its organizational strategy.
a. Uncertainty of Customer Demand
Here is the complicating factor: It is difficult to know what customer requirements will be from day to day, month to month, quarter to quarter, and so on. For instance, if a manufacturer was guaranteed that its wholesale or retail customers were going to need 1,000 SKUs (stock keeping units) every Wednesday afternoon, then getting those products to customers at the right time and place would be a matter of simple calculation based upon lead times for production and delivery. In turn, the manufacturer would look at the bill of material, determine the lead time for each, and submit schedules to its suppliers. Unfortunately, it’s difficult to predict even the most stable demand—say, for a product like diapers. There is some variability in demand for diaper, even though they aren’t subject to seasonal style changes or rapid peaks and valleys in response to outside influences affecting ability to pay. (That’s why Procter & Gamble cooperates with Wal-Mart to plan for demand and replenishment of diapers.) The chain of demand begins at the far retail end of the supply chain and works its way back toward the source of raw materials used in making the product. The traditional way of attempting to satisfy this demand is to forecast it.
b. Developing a Supply Chain Strategy for Improving Forecast Accuracy
In this retail example, forecasting along the chain works like this:
- The retailer forecasts demand from parents who purchase diapers.
- The wholesaler forecasts demand from all its retailers.
- The manufacturer forecasts demand from the wholesale distributors.
- The component suppliers forecast demand from manufacturers.
- The raw materials suppliers forecast demand from the component manufacturers.
c. Analyzing the Impact of Demand Fluctuations on Supply Chain Strategies & Bullwhip Effect
How effective is this supply chain strategy? Let’s say you don’t want to be placing large bets on the accuracy of all those forecasts. Here’s what actually happens:
Parents vary their diaper-buying patterns in fairly small increments due to . factors nobody fully understands. They may go to different stores for a change, shop on Tuesday instead of Wednesday, or buy two or three weeks’ worth at one time because the diapers are on sale. So, actual demand never quite meets the forecast.
Meanwhile the retailer had already ordered enough to allow a little extra “safety stock” to put in its storeroom. (For retailers, safety stock is a quantity of stock planned to be in inventory to protect against fluctuations in demand or supply.) Or maybe the retailer runs a promotion that is not communicated to the distributor, thus resulting in needing a larger order than was previously forecasted. These fluctuations impact forecasting for the distributor.
The wholesale distributor had forecasted demand based on past orders from its retailers. But now those demand patterns have a wider variability than the demand pattern at the retailer’s checkout counters due to that safety stock the retailer held on to. Sometimes the safety stock accumulates because demand is less than the forecast, and this means that the retailer’s next order is for less than its forecast—or perhaps it doesn’t have to order at the usual time at all, because it has a glut of diapers—which it probably sells off in a promotion. The upshot of all this is that the small variations in end-user demand are magnified at the distributor.
- Up the chain, the manufacturer of those diapers looks at the demand pattern from the distributor and makes its own forecasts, which show an even wider swing in variability.
- And this variability goes up the chain with ever-wider swings.
This pattern of variability is called the bull-whip effect, and it affects all manner of supply chains that are based on serial forecasting by each independent division or firm that touches the product as it travels from raw material to finished retail item.
Strategy # 3: Demand Driven Enterprises
a. Demand-Driven Supply Chain Model: Bull-Whip Effect
The next organizational strategy we’ll look at is the demand-driven enterprise. The bull-whip effect is driven by demand forecasts; the solution is to replace the forecasts with actual demand information. This isn’t necessarily a simple matter either, but supply chain professionals have evolved techniques for letting actual orders (not forecasts) drive production and distribution. In the demand-driven chain, supply management is focused on customer demand. Instead of manufacturers planning their operations based on factory capacity and asset utilization, the demand-driven supply model operates on a customer-centric approach that allows demand to drive supply chain planning and execution—moving the “push-pull frontier,” as it’s called, back up the chain at least to the factory. Instead of producing to the forecast and sending finished products to inventory, the production process is based on sales information. There is, in other words, no fixed production schedule in a strictly demand-driven supply chain. Product is turned out only in response to actual orders, “on demand,” in other words. (Note, however, that on the supplier side of the plant, forecasts still determine delivery of raw material. The art of forecasting remains crucial, even in a demand-driven chain.)
b. Transitioning from Push to Pull: Challenges and Strategies
Everything in a push system is pushed downstream from one point to the next according to schedules based on the forecasts. The supplier delivers components in the amounts determined by the schedule to inventory, where they await use in manufacturing. The plant turns them into finished products and pushes the products to the distribution center or the retailer, where they await an order from downstream.
The challenge in changing from forecast-driven (push) to demand-driven (pull) systems is in reducing inventory without also lowering customer satisfaction. When a demand-driven system is set up and managed properly, it can enhance customer service while reducing costs. But stockouts are a risk.
c. Strategies for Mitigating Demand Uncertainty
As always with supply chains, the decision to switch to a demand-pull process trades one type of risk for another:
- In the forecast-push process, the risk is related to the build-up of inventory all along the chain.
- Not only does inventory cost money while it sits in a retail stockroom, distribution center, or preproduction storage area;
- it runs the risk of becoming Obsolete or irrelevant for a number of reasons.
Examples
- In a world of sapid innovation, inventory obsolescence is a very real threat. (For example, Cisco Systems, for years an exemplar of successful and innovative supply chain management, had to dispose of US$2.25 billion worth of useless inventory when the dot-coin bubble burst at the beginning of this millennium. All those season close-out sales you see in clothing and department stores are a way of clearing out the overstock. Bookstore remainder tables (which are much less in evidence than they were a decade or two in the past) are a sign of inventory overhang caused by failed forecasting.
- Magazine distributors used a supply chain strategy to destroy huge quantities of monthly magazines 12 times a year when they came back from retail outlets. (Since magazines are inexpensive to produce and destroy compared to their retail price, the distributors would rather destroy ten copies than miss one sale.) Those are the results of producing to forecasts that no one trusts and purposely overstocking to be sure of meeting unexpectedly high demand.
- In the demand-pull, make-to-order model, on the other hand, the risk is that orders will begin to come in above capacity and al/ along the chain there will be expensive activity to run the plant overtime, buy more and faster transportation, or sweet-talk customers into waiting for their orders to be filled or substituting a different product. (Running short of stock is also a risk in the forecast-driven chain. Forecasts can be wrong in either direction. That’s why the safety stock builds up at each point where orders come in.) One technique to prepare for uncertain demand is kitting, which is preparing (making/purchasing) components in advance, grouping them together in a “kit,” and having them available to assemble or complete when an order is placed.
d. Transforming to a Demand-Driven Enterprise: Challenges and Best Practices
In Gartner’s annual supply chain report, they rank the top 25 demand-driven supply chains, thereby underscoring the importance of this strategy. In fact, the companies that gain a position on this list have all applied demand-driven principles to coordinate supply, demand, and product management to better respond to market demand. If you would like additional information about this report, a link is provided in the online Information Center.
In reality, most organizations pursue a push-pull supply chain strategy and the point where push moves to pull is the key strategic decision. Once that decision has been made, building a demand-driven enterprise can require significant changes in all supply chain processes.
e. Building Trust and Collaboration
The following are some major steps:
Step-1: Access to Real Data
Provide access to real demand data along the chain for greater visibility of the end customer. The first requirement is to replace the forecasts with real data. The only supply chain partner with access to these data first hand is the retailer, and retailers in the past have been no more willing to share business data than any other firms. The other partners lack “visibility”—one of the main supply chain principles. They simply cannot see what’s going on with the end customer. But visibility supply chain strategy is a necessity for building a pull system, and pioneers like Wal-Mart have led the way in that regard. With point-¬of-sale scanning or radio frequency identification (RFID), a retailer can alert its suppliers to customer activity instantaneously. Instead of producing to the monthly forecast, manufacturers with that kind of immediate signal from the front lines can plan one day’s production runs at the end of the preceding day. They produce just enough to replace the sold items.
Step-2: Enhance Collaboration
Establish trust and promote collaboration among supply chain partners. Collaboration is implied in the sharing of information. But more is at stake than simply sharing sales information. Partners may have to invest in new technology and develop new systems to be able to use the real-time data. With orders going out without a schedule, all processes will have to be altered—warehousing (storage no longer needed), packaging, shipping, and planning will all be handled differently in the new system. In return for receiving real-time data that allow reduction of inventory; suppliers and distributors have to agree to change their processes in whatever ways may be necessary to make the new system function without disrupting customer service.
Step-3: Increase Agility
Increase agility of trade partners. Because the inventory buffers will not exist or will be much reduced in this demand-driven supply chain, the trade partners need to develop agility—the ability to respond to the variability in the flow of orders based on sales. The plant, for example, may have to undergo considerable change if it has to produce several different kinds of products under the new circumstances. When making to forecast, a plant can run a larger volume of each product to send to inventory. But when making to order, the plant may have to produce several different types of products in a day. There will be no room for long changeover times between runs of different products; therefore, equipment, processes, work center layouts, staffing, or siting—or all these things—may have to change to create the capacity required to handle the new system.
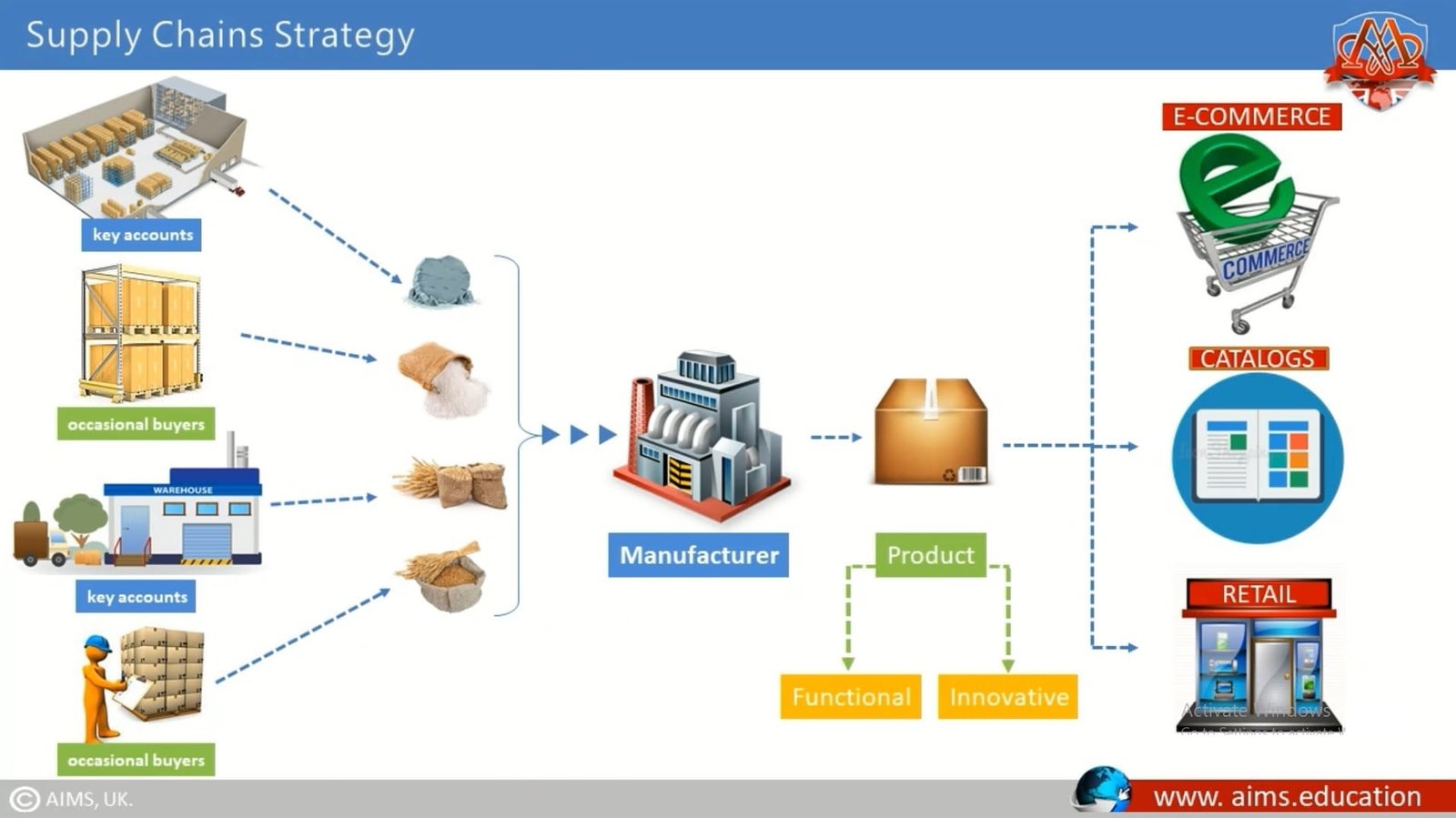
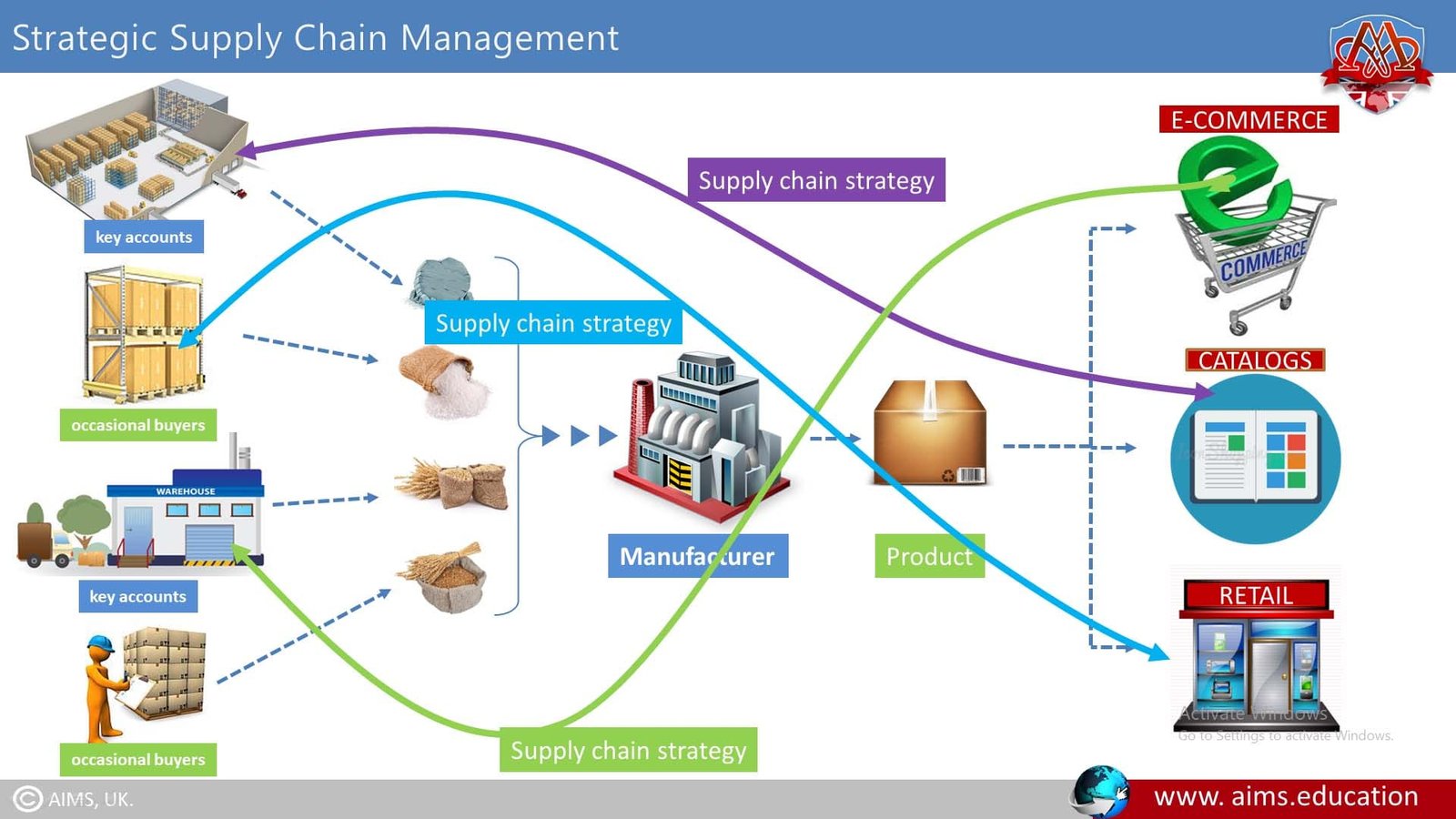
Strategy No. 4: Number of Supply Chains
a. Optimising Supply Chain Strategies for Diverse Product Lines
The last strategy we’ll cover is based on a company having more than one supply chain, depending upon the number and types of products that are passing along the chain and other variables. For a product with a complex bill of material (many parts that combine into many components to make the final product), a manufacturer may be bringing in materials from many suppliers. And these materials might range from low-priced commodities to fragile or sophisticated materials that require special shipping and handling. Suppliers might range from small specialized firms to raw materials giants larger than the manufacturer. Some are key accounts; some might be occasional buyers. The finished products may be sold through several different channels—c-commerce, printed catalogs, commercial, and retail. These variables may combine in different ways, each suggesting its own type of supply chain strategy. Next we’ll explore how product types, functional versus innovative, often require different supply chain strategies.
b. Supply Chain Strategies: Functional vs. Innovative Products
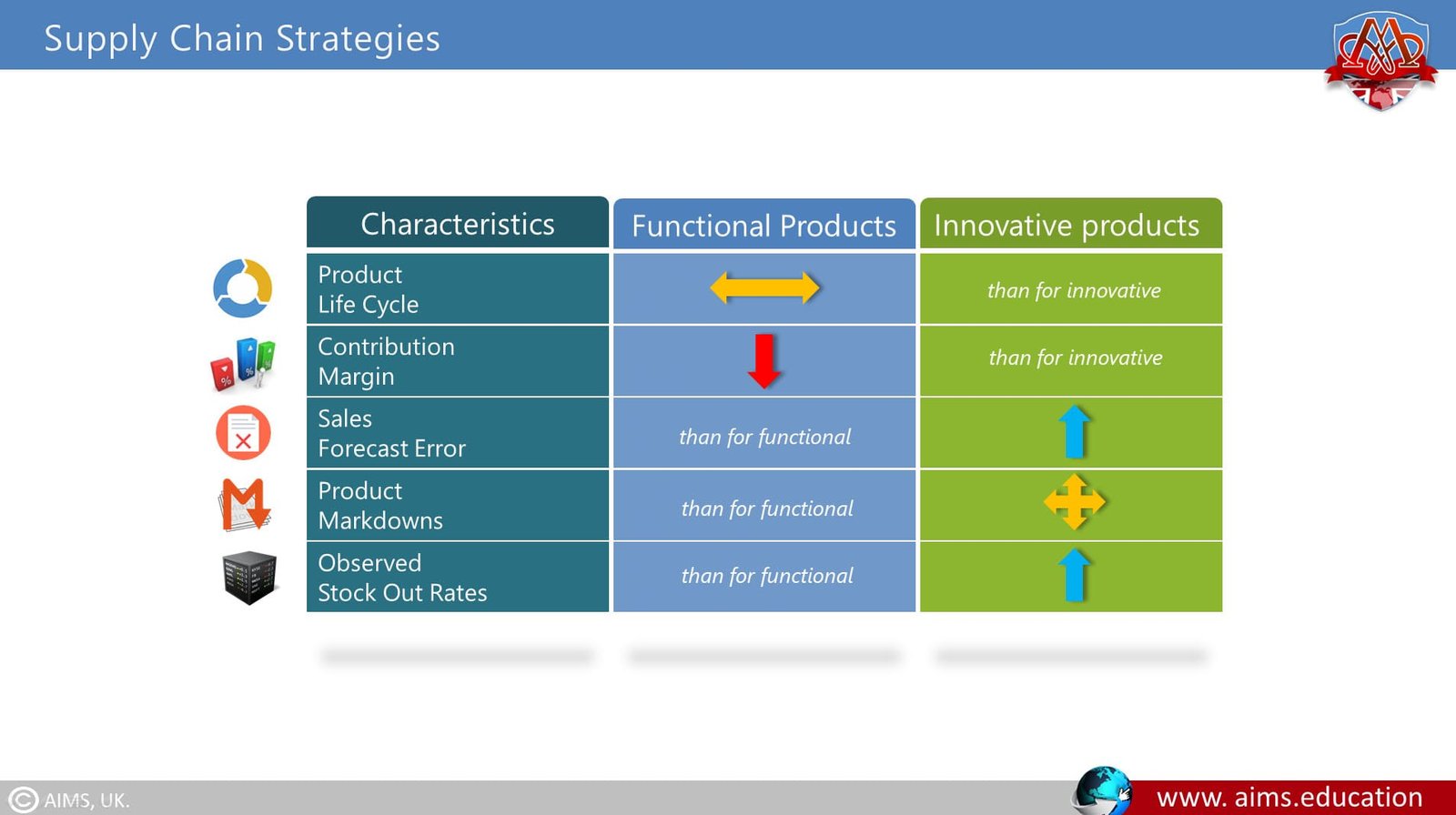
In “What Is the Right Supply Chain for Your Product?” Marshall L. Fisher distinguished two types of products, functional versus innovative, that require different supply chain strategies. Functional products that change little from year to year have longer life cycles (perhaps more than two years), relatively low contribution margins, and little variety. Because demand for them is stable, they are fairly easy to forecast, with a margin of error of about 10 percent, very few stockouts, and no end-of season markdowns.
c. Supply Chain Strategy for Cost Efficiency and Performance
The appropriate supply chain for these products should emphasize predictability and low cost with performance indicators such as the following:
- High average utilization rate in manufacturing.
- Minimal inventory with high inventory turns.
- Short lead time (consistent with low cost).
- Suppliers chosen for cost and quality.
- Product design that strives for maximum performance and minimal cost.
d. Challenges for Innovative Products and Make-to-Order Functional Products
However, make-to-order functional products, such as replacement parts for customized equipment, usually have long lead times (six months to a year). Innovative products have unpredictable demand, relatively short life cycles (three months for seasonal clothing), and high contribution margins of 20 to 60 percent. They may have millions of variants in each category, an average stockout rate from 10 to 40 percent, and end-of-season markdowns in the range of 10 to 25 percent of regular price. The margin of error on forecasts for innovative products is high-40 to 100 percent—but the lead time to make them to order may be as low as one day and generally is no more than two weeks.
e. Supply Chain Strategies for Innovative Products
The supply chain for innovative products should emphasize market responsiveness rather than physical efficiency, with performance indicators such as the following:
- Excess buffer capacity and significant buffer (or safety) stock of parts or finished items.
- Aggressive reduction of lead times.
- Suppliers chosen for speed, flexibility, and quality (rather than cost).
- Modular design that postpones differentiation as long as possible.
Innovative products, with their high margins and unpredictable demand, justify the extra expense for holding costs. (Fisher also proposes, however, that manufacturers of innovative products can look for other solutions to the problem of unpredictable demand, such as aggressively reducing lead times and producing products to order rather than for inventory.)
f. Dual Nature of Products: Innovation vs. Functionality
Here is a conundrum… What happens when a product can fall into either category? Fisher says that some products can be either innovative or functional. Automobiles fit that description, with a low-priced, no-frills car like a base model Chevrolet Cobalt or Hyundai Excel representing the functional end of the spectrum and a Porsche representing the other end. Similarly, coffee can be functional—as anyone who has worked in an office knows, in which case it should be available quickly at a low price with perhaps cream and sugar as options. At a high-end coffee shop, on the other hand, patrons are willing to endure longer lead times and pay more money for their coffee, but they want variety in return.
g. Diversifying Supply Chain Strategy for Innovation and Functionality
The idea that the same type of product can be either functional or innovative implies that one company might have more than one supply chain. And that’s the contention of Jonathan Byrnes, a professor at MIT. Writing in the Harvard Business School’s Working Knowledge, Byrnes asserts that one supply chain is not enough; two, three, or more would be preferable. “One size fits all” supply chains may have been sufficient in the past, he believes, when that was the competitive norm, but new information technology makes it possible to have multiple, dynamic chains that can accommodate different product and information flows.
h. Supply Chain Strategies for Different Product Types
Byrnes breaks products into three categories: staples, seasonal products, and fashion.
Staples (which are much like Fisher’s functional products) have steady, year-round demand and low margins. White underwear is an example. Byrnes advises stocking staples only in retail outlets in small quantities and transporting them in truckload quantities. (A full truck, is more cost-effective for the shipper than a partially loaded vehicle.)
Seasonal products could include outdoor patio furniture, holiday decor, etc., for which the demand is more predictable since it is tied to the holiday season.
Fashion products are like Fisher’s innovative items, with unpredictable demand. Zara, the Spanish clothing manufacturer, has two supply chains, one for staples and the other for fashion clothing. To get the fastest response time, Zara uses European suppliers for the fashion items. But for the more predictable demand items, it uses eastern European suppliers that have poor response time (not a concern) and lower cost.
i. How to Align Business Plans with Demand Dynamics?
In addition to varying the supply chain by product type, Fisher recommends several other variables to consider—store type and time in season or product cycle. Demand varies considerably over the life cycle of many products. The same item might have infrequent demand at first, more stable demand in its maturity phase, and falling demand at the end of its life cycle. With more than one supply chain, the nucleus firm can move its products from one chain to the other in response to changing variables, such as type of channel or life-cycle stage. Business and organizational strategies are formalized and clearly specified within an organization’s business plan, so this is discussed next.
Supply Chain Strategy in Business Success
The supply chain has the overarching goal of providing customers with goods and services when they want them, at a competitive price, while being consistent with the organization’s and extended supply chain’s strategies. If the supply chain cannot successfully execute this supply chain strategy, the business, or product line, may cease to exist.
When you think about the role the supply chain plays in the bigger context of your company, the functional strategies underlying supply chain management must articulate with the business plan, and remember also that the purpose of supply chains is to be globally competitive. Time, distance, and collaboration are basic elements in modern supply chains that impact the chain’s ability to respond to competitive changes in the global marketplace. The relationships of time, distance, and collaboration weave like three bright threads through the fabric of any supply chain on the globe. Therefore, collaborative relationships are explored further as they are a primary component of supply chain strategy.
Key Advantages of Developing a Supply Chain Strategy
Here are the key advantages of developing a supply chain strategy:
- Competitive Advantage.
- Enhanced Speed and Efficiency.
- Increased Value Delivery.
- Flexibility and Adaptability.
- Strategic Resource Utilization.
- Investor and Customer Satisfaction.
These benefits underscore the strategic importance of supply chain management as a pivotal factor in an organization’s success. Further insights into these strategies, alongside specialized training, are part of comprehensive supply chain management courses and MBA focusing on supply chain management, such as those offered by AIMS.
How to Choose the Right Supply Chain Strategy?
Below are steps to guide businesses in selecting the most suitable supply chain strategy:
- Assess Your Business Goals.
- Analyze Your Market Demand.
- Evaluate Your Product Characteristics.
- Consider Your Environmental Impact.
- Analyze the Competition and Industry Best Practices.
- Review Your Resources and Capabilities.
- Develop a Risk Management Plan.
- Run Pilot Tests.
- Implement the Strategy.
- Regular Review and Adapt changes.
