What is Project Communication Management?
Project Communication Management is a collection of processes that ensures that communication in the project is sent, received, and understood by all project team members and stakeholders precisely at the right time. Project managers should ensure that the right tools and techniques are used to design the project management communication plan and that it is monitored and reviewed regularly to ensure minimum misunderstandings and conflicts within the project. Project managers spend most of their time communicating with team members, and other project stakeholders, whether it is internal or external to the organization. It is found that:
- Communication in project management consumes 90 percent of a Project Manager’s time, and,
- 55% of communication in project management is non-verbal.
Benefits and Importance of Communication in Project Management
The following key points highlight the importance of project communication management:
- Project communication management helps clarify project goals and project team members’ and stakeholders’ roles and responsibilities.
- It ensures that all stakeholders receive timely updates about the project’s progress and any potential issues or misunderstandings.
- It facilitates informed decision-making by providing relevant information to the right team member or stakeholder at the right time.
- Open and transparent project communication enhances engagement and trust among stakeholders.
- Transparent and timely communication helps in the early identification and resolution of conflicts within the team.
- Using better communication, project team members can efficiently coordinate resources.
- Everyone in the team knows others’ current tasks and responsibilities.
- Project risks are communicated on time when addressed, which improves prompt project risk management.
Key Project Communication Skills You Should Have?
As a project manager, you should have the following project communication skills:
- Listen actively and effectively to team members and project stakeholders.
- Question and probe ideas to ensure better understanding.
- Educate to increase the team’s knowledge so that they can perform better.
- Fact-finding to identify or confirm information.
- Set and manage expectations and clarify project management objectives.
- Persuade a person, a team, or an organization to act.
- Motivate to provide encouragement or reassurance.
- Coach team members to improve their performance and achieve desired results.
- Negotiate to achieve mutually acceptable agreements between parties involved in the project.
- Resolve conflict to prevent disruptive impacts and;
- Should be able to summarize, recap, and identify the next steps in your project.
Important Questions in Project Communication Management
During the project communication management, you should follow these considerations and take them into account:
- Who needs what information? And who is authorized to access that information?
- What information may be required by any person in the project?
- Where will you be storing the information?
- In which format will you be storing the information?
- How will the information be retrieved? and;
- How will you manage the time zone, language barriers, and cross-cultural considerations for effective communication in your project?
Project communication management is part of the Certified Project Manager (CPM), an online project management certification, diploma for project management, and online MBA in project management programs. These are career-oriented qualifications designed to develop knowledge and skills in projects, programs, and project portfolio management.

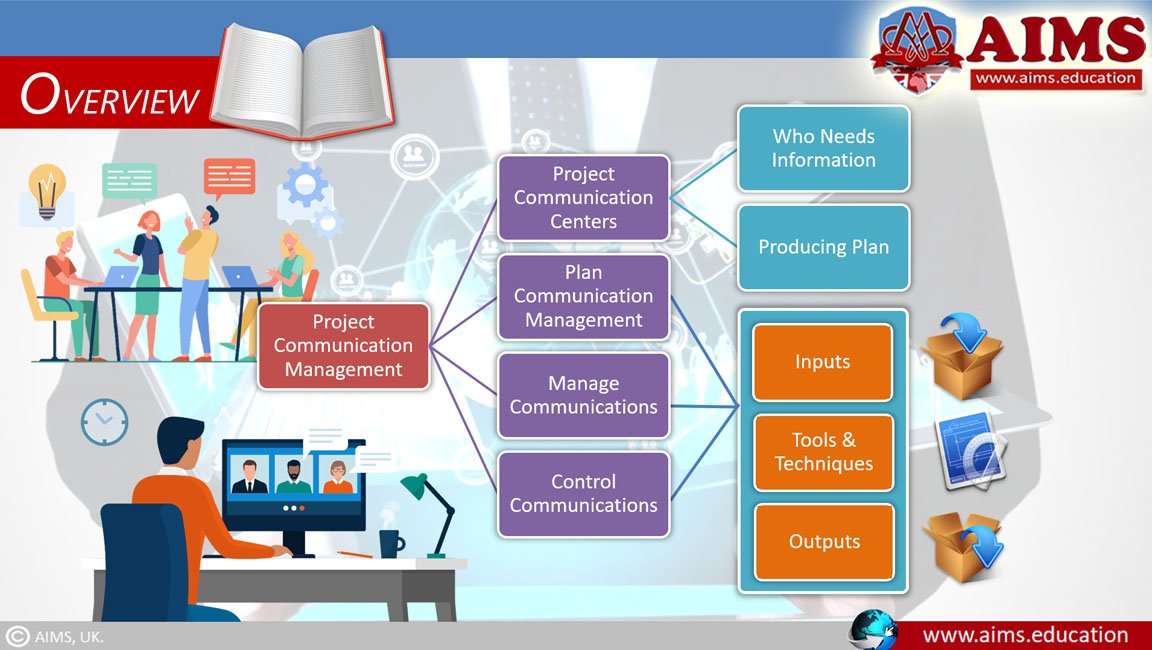
Introduction to Project Communication Management Processes
Here is an overview of the three processes that are involved in the Project Communications Management:
1. Plan Communications Management
Project management communication plan describes how communications will flow in your project and how you will manage your project’s communication strategy. The plan communication management process must document communications requirements throughout the project management phases. The project management communication plan should be based on stakeholders’ information, needs and requirements, as well as available organizational resources.
Inputs to Plan Communication Management
Key inputs to the project management communication plan process are:
- Stakeholder Register,
- Stakeholder Management Strategy,
- Enterprise Environmental Factors, and,
- Organizational Process Assets.
Tools and Techniques for Project Management Communication Plan
The following tools and techniques are used during the project management communication plan process are:
- Communication Requirements Analysis,
- Communication Technology,
- Communication Models, and,
- Communication Methods.
Outputs of Plan Communication Management
Here are the outputs of the Plan Communication Management process:
- Communication Management Plan,
- Project Management Plan Updates, and,
- Project Documents Updates.
2. Manage Communication
When all stakeholders agree on the communication plan in project management, the Manage Communication process is used to create, collect, distribute, store, retrieve, and ultimately dispose of the project information in accordance with the communications management plan.
Key Benefits
“The Manage Communication process process enables an efficient and effective communication flow between project stakeholders”.
Inputs to Manage Communication Process
Inputs to the manage communication process in project communication management are:
- Project Communication Management Plan,
- Work Performance Reports,
- Enterprise Environmental Factors, and,
- Organizational Process Assets.
Tools and Techniques for Manage Communications Process:
The following are important considerations and tools used in the Manage Communications process:
- Communication Technology,
- Communication Models,
- Communication Methods,
- Information Management Systems, and,
- Performance Reporting.
Outputs of Manage Communications Process
Here are the outputs of this process are:
- Project Communications,
- Report Management Plan Updates,
- Project Document Updates, and,
- Organizational Process Assets Updates.
3. Control Communications
This is the third and last process of the project communication management. This process monitors and controls the communications throughout the entire project life cycle, and it ensure that the information needs of the project stakeholders are met.
Key Benefit
“The Control Communications process ensures an optimal information flow, among all communication participants in the project to communicate, at any moment of time”.
Inputs to Control Communication Process
Key inputs to the control communication process are:
- Project Management Plan,
- Project Communications,
- Issue Log,
- Work Performance Data, and,
- Organizational Process Assets.
Tools and Techniques for Control Communications:
Tools and techniques used to control communication in the project are:
- Information Management Systems,
- Expert Judgment, and,
- Meetings.
Outputs of Control Communications
The final outputs of the Control Communication process in the project communication management are as follows:
- Work Performance Information,
- Change Requests,
- Project Management Plan Updates,
- Project Documents Updates, and,
- Organizational Process Assets Updates.

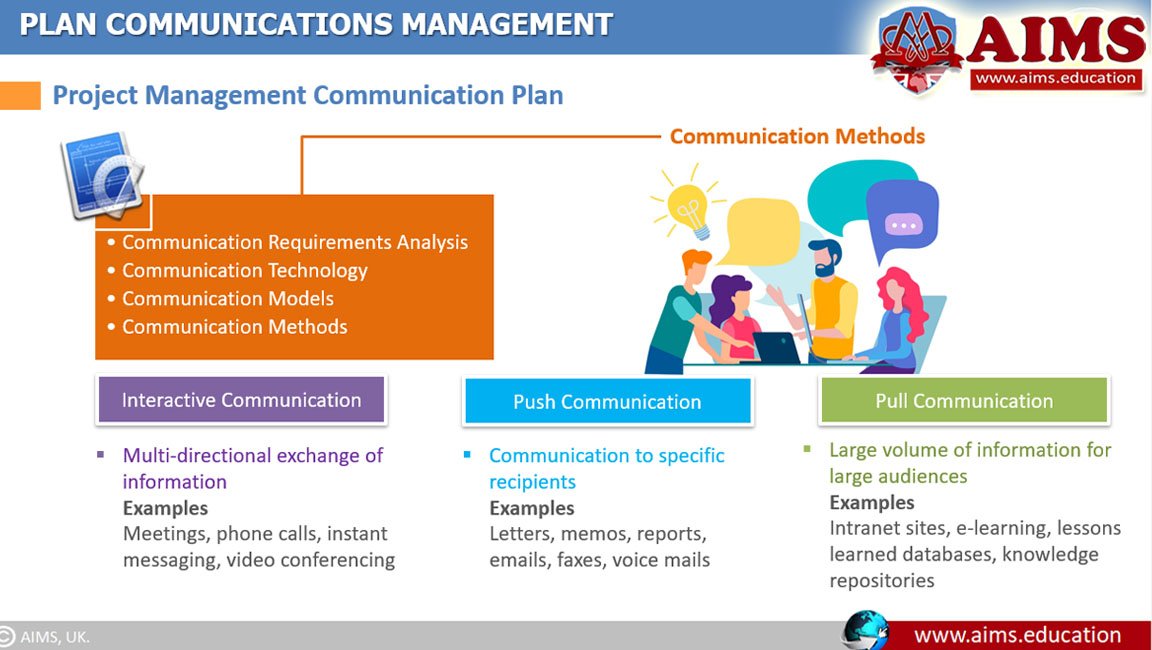
Types of Project Communication Management Methods
Several project communication management methods are used to share information among project stakeholders. They are broadly classified into the following three categories:
- Interactive communication.
- Push communication.
- Pull communication.
1. Interactive Communication
It is a type of project communication between two or more parties, performing a multi-directional exchange of information through an efficient way. Examples of Interactive communication are: Meetings, phone calls, instant messaging, video conferencing, etc.
2. Push Communication
Push Communication is the communication to specific recipients, who need to receive the information. Examples are: Letters, memos, reports, emails, faxes, voice mails, etc.
3. Pull Communication
Pull Communication is usually a large volume of information for large audiences. In other words, it is about providing group access to common information. Examples of such type of project management communications methods are Intranet sites, e-learning, lessons-learned databases, knowledge repositories, etc.
9 Key Elements and Tools in Project Communication Management
1. Sources of Information
Sources of information typically used to identify and define project communication requirements. They include the following:
- Organizational charts;
- Project organization and stakeholder responsibility relationships;
- Disciplines, departments, and specialities involved in the project;
- Logistics of or project hr management, that is, how many persons will be involved with the project? and at which locations?
- Internal information needs, for example, when communicating within organizations?
- External information needs, for example, when communicating with the media, public, or contractors? and,
- Stakeholder information and communication requirements, from within the stakeholder register.
2. Communication Technology
Communication technology refers to the tools, systems, and equipment that are used to transfer different information to the stakeholders of the project during the project communication management.
For Example:
- A project team may use techniques from brief conversations to extended meetings or from simple written documents to extensive materials.
- This tool includes a variety of well-known options such as e-mail, phone calls and face-to-face meetings.
3. Communication Models
Communication models depict how information is transmitted during the project communication management from the sender, and how it is received by the receiver.
- The sender of information is responsible for making the information clear and complete.
- The receiver is responsible for making sure that all of the information has been received and understood.
4. Communication Theory
The communication theory is also considered when making the project management communication plan. The factors that influence the choice of communications technology are as follows:
- Urgency of the information;
- Availability and reliability of technology;
- Ease of use if communications technology is unfamiliar to users;
- Project environment and location of members;
- Confidentiality of information; and;
- Organizational culture.
4. Information Management Systems
During the project communication management, the project information and communication in project management are managed and distributed using a variety of tools. They include Hard Copy Document, Electronic Communication, and Electronic Project Communication Management Tools. Here is a short overview of these tools.
a. Hard-Copy Document Management
They include letters, memos, reports, and press releases.
b. Electronic Communications Management
They include E-mail, fax, voice mail, telephone, web conferencing, websites, and web publishing.
c. Electronic Project Management Tools
The electronic tools that are used for project communication management include the following:
- Web interfaces to scheduling and project management software,
- Meeting and virtual office support software,
- Online Portals, and,
- Collaborative work management tools.
5. Performance Reporting
The performance information, that is, the comparison of the actual work with the planned work, is presented in a work performance report. These reports are shared with relevant stakeholders on a regular basis. Managers should also be prepared to send out information as requested by key stakeholders. Report format may range from a simple status report, such as percent complete, or status dashboards for each area.
More elaborate reports in the project communication management may include:
- Analysis of past performance,
- Analysis of project forecasts,
- Current status of risks and issues,
- Work completed during the period,
- Work to be completed in the next period, and,
- Summary of changes approved in the period.
6. Lesson Learned Register
If challenges related to communication in project management are encountered, the following information is added to the lesson-learned register:
- How those challenges could have been avoided? and,
- How did an improved approach work well during the project communication management?
7. Information Management System:
An information management system provides a set of standard tools to capture, store, and distribute information to the project stakeholders, about managing the projects costs, shedule and time management in projects, quality management in projects, and performance. Software like Microsoft Project is used to storing and distributing information on the project.
Examples of distribution formats are:
- Table reporting,
- Spreadsheet analysis, and,
- Presentations.
8. Expert Judgement
This method is used to assess the impact of project communications, and take actions based on the contents of those communications. Expert judgment may be provided by any group or individual with specialized knowledge, such as:
- Other units within the organization,
- Consultants,
- Stakeholders, including customers or sponsors,
- Professional and technical associations,
- Industry groups,
- Subject matter experts, and.
- Project management office.
9. Meetings
The Control Communications process requires discussion with the project team, to determine the most appropriate way to update project performance, and communicate to stakeholders during the project communication management. Project meetings include discussions with: Suppliers, vendors, and other project stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is project communication management?
It is the set of processes that ensure information is created, shared, received and understood by the right stakeholders at the right time across a project’s life cycle.
Q2: How does a project communication plan work?
It defines audiences, channels, cadences, formats, storage and access, and responsibilities—so messages reach the right people in the right way and time.
Q3: What are the key benefits of communication in project management?
Clear goals and roles, timely updates, better decisions, stronger trust, faster conflict resolution, coordinated resources, visible risks, and quicker issue handling.
Q4: What should a project management communication plan include?
Stakeholder needs, requirements, channels, cadences, templates, storage and access methods, responsibilities, and change control for updates.
Q5: Which processes make up project communication management?
Plan Communications Management, Manage Communications, and Control Communications.
Q6: What are interactive, push, and pull communication methods?
Interactive is two-way (meetings, calls). Push sends info to specific recipients (email, reports). Pull provides shared access (intranet, repositories).
Q7: How do you choose communication technology for a project?
Consider urgency, reliability, ease of use, team location, confidentiality, and culture to select tools that fit the context and stakeholders.
Q8: What does the Manage Communications process produce?
Project communications and updates to reporting and project documents, aligned with the agreed communications plan.
Q9: How does Control Communications improve outcomes?
It monitors message quality, timing, channels, and feedback, then adjusts the plan to keep information flowing optimally.
Q10: What common communication mistakes should teams avoid?
Undefined audiences, inconsistent cadences, channel overload, no central repository, poor meetings, and ignoring time zones or language.
Q11: Which tools support project communication management?
Email and messaging, video conferencing, document management, dashboards, PM software, portals, and collaboration suites.
Q12: What performance information should be reported?
Status vs plan, forecasts, risks/issues, completed and upcoming work, and approved changes in clear dashboards or reports.
