What is Project Management Organizational Structure?
The project management structure is an enterprise environmental factor that determines how the organization and project manager should perform. Essential to this is the project organizational structure, the underlying framework that governs how projects are carried out within a company. The heart of efficient project management lies in the way an organization structures its project teams, and the project teams are structured using one of three ways: Functional, Projectized, or Matrix. These project management organizational structures come with varying levels of agility, control, and communication.

Types of Project Management Structure:
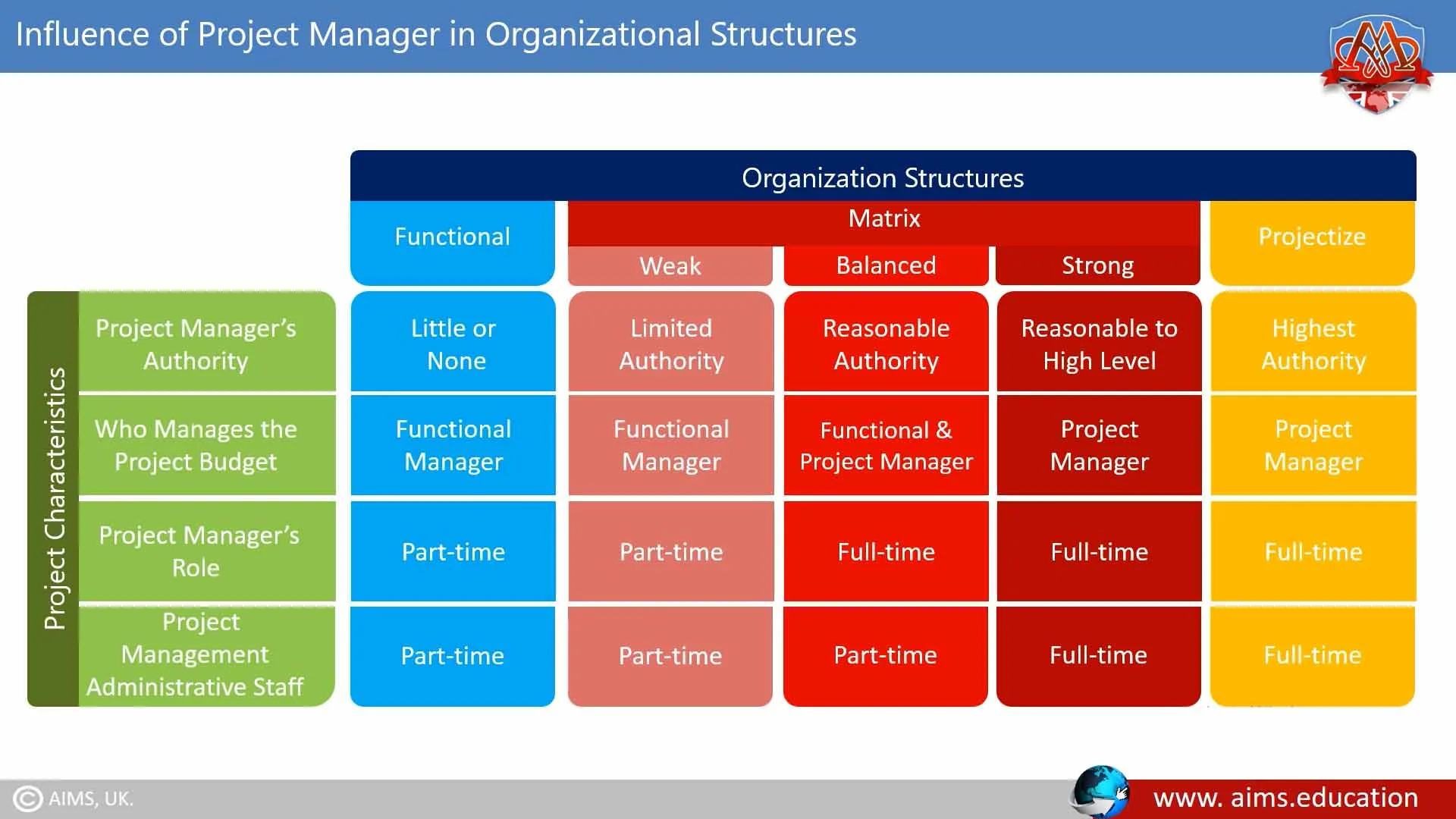
Organizations have their own styles and cultures that influence how project work is performed. One of the keys to determining the type of organization you work in is measuring how much authority senior management is willing to delegate to project managers. We’ll now take a look at each types of organizations individually to better understand how the project management role works in each one.
1. Functional Organizational Structure:
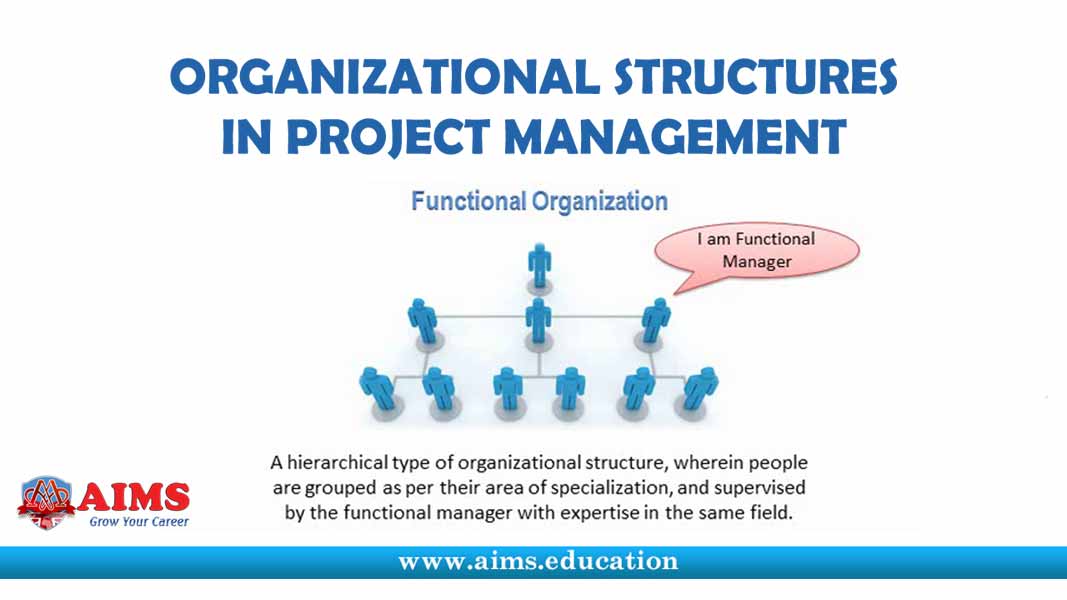
A functional project organization structure is a hierarchical type of project management structure wherein people are grouped as per their area of specialization and supervised by the functional manager with expertise in the same field, so that their skills can be effectively utilized and the organization’s objective can be achieved.
Here, all authority, budget allocation, and decision making power stays with the functional manager. A project manager has no role in this type of structure. Even if he exists, his role will be very limited and he has to ask the functional manager for his requirements. Here, a project manager may have the title of a coordinator or an expediter.
Key Features of Functional Project Management Structure
The Functional project management structure is suitable for an organization that has ongoing operations such as manufacturing and production operations. In the functional project organizational structure, the organization is divided into various specific departments; e.g. human resource, marketing, finance, operations, etc. Each department will have its own department head and he will be responsible for the performance of his section. This helps control the project quality and uniformity of performance.
I. ADVANTAGES OF FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE:
Following are a few advantages of functional organizations:
- Employees are grouped according to their knowledge and skills.
- Job responsibilities and reporting are straight to the functional head, and the hierarchy path is clear.
- Employees have a clear career growth path.
- Within the functional department, communication, cooperation, and coordination are excellent.
II. DISADVANTAGES OF FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE:
The following are a few disadvantages of functional organizations:
- The employee may become lazy due to repeating the same type of work.
- Conflicts may arise due to the promotion of another employee.
- The functional manager pays attention only to his department; he usually doesn’t care for other teams or sections.
- Poor communications and poor inter-department coordination.
- Delays in decision-making due to bureaucratic hierarchy.
“In the functional project organizational structure, the organization is divided into various specific departments; e.g. human resource, marketing, finance, operations, etc. Each department will have its own department head and he will be responsible for the performance of his section. This helps control the quality and uniformity of performance”.
Key Note!
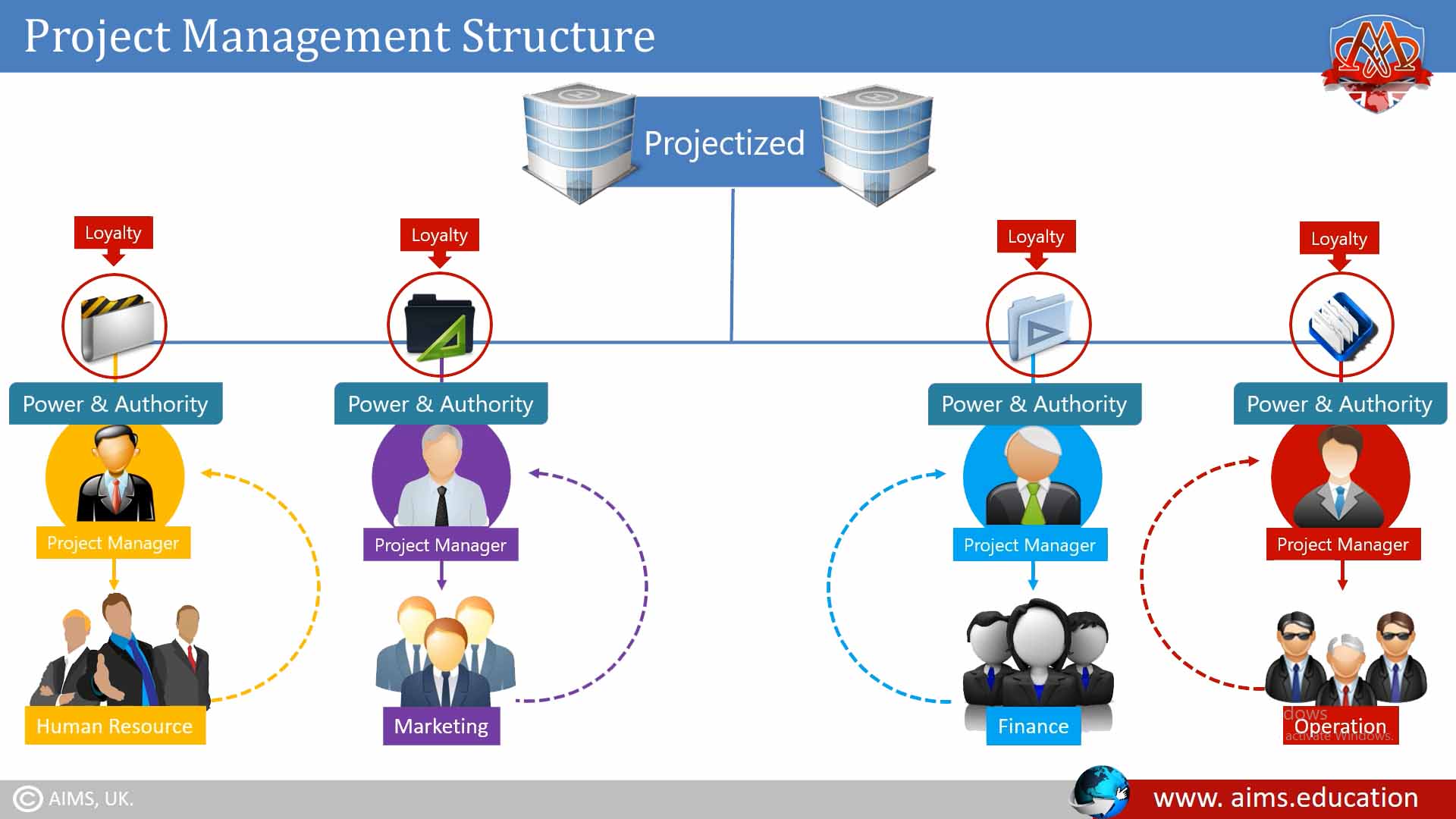
2. Projectized Organizational Structure:
Projectized organizations are nearly the opposite of functional organizations. The focus of this type of organization is the project itself. The idea behind a projectized organization is to develop loyalty to the project, not to a functional manager. In a projectized project management organizational structure, the project manager has all the power and authority, and everybody directly reports to the project manager. Here, either no functional manager exists, or if he exists, he will have a very limited role.
I. ADVANTAGES OF PROJECTIZED STRUCTURE:
A few advantages of projectized project management organizational structure are as follows:
- Clear line of authority.
- Strong communication with single reporting system.
- Flexibility in trade-offs and decision making.
- Fast decision making.
II. DISADVANTAGES OF PROJECTIZED STRUCTURE:
A few disadvantages of projectized project management structure are as follows:
- Authority and power can make project managers arrogant.
- The work environment can be stressful because there is always a deadline (milestones).
- Team members have a sense of insecurity because, once the project finishes, they may lose their jobs.
- If the project gets elongated, the cost of employees and equipment can go higher.
“In projectized organization, the project manager has all the power and authority and everybody directly report to the project manager. Here, either no functional manager exists, or if he exists, he will have a very limited role.”.
Key Note!
3. Matrix Organizational Structure:
Matrix organizations came about to minimize the differences between, and take advantage of, the strengths and weaknesses of functional and projectized organizations. The idea at play here is that the best of both organizational structures can be realized by combining them into one. The project objectives are fulfilled and good project management techniques are utilized while still maintaining a hierarchical structure in the organization.
Key Features of Matrix Project Management Structure
In a matrix project organization structure, the knowledge and skills of the talented employees could be shared between the functional departments and the project management teams, as needed. Here, the employee generally works under two bosses. The authority of the functional manager flows vertically downwards, and the authority of the project manager flows sideways. Since the authorities flow downward and sideways, this structure is called the Matrix Organization Structure. In a matrix project organizational structure, employees usually have two bosses to whom they may have to report. Which boss is more powerful depends upon the type of matrix structure.
Types of Matrix Project Organizational Structures
Matrix organization structure can be further divided into three categories:
- Strong Matrix: The balance of power leans more toward the project manager’s responsibilities.
- Balanced Matrix: Power is equally distributed between functional managers and project managers.
- Weak Matrix: Functional managers hold more power over projects.
I. ADVANTAGES OF MATRIX ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE:
- Enhanced communication.
- Better resource utilization.
- Adaptability to shifting priorities within a project.
II. DISADVANTAGES OF MATRIX ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE:
- Confusion over roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines.
- Conflict between project and functional managers.
- A high level of bureaucracy can affect decision-making.
“In matrix structures, usually employees have two bosses to whom they may have to report. The authority of the functional manager flows vertically downwards and the authority of the project manager flows sideways. Since, the authorities flow downward and sideways, this project management structure is called the Matrix Organization Structure. Which boss is more powerful depends upon the type of matrix structure.”
Key Note!
How to Choose the Right Project Organizational Structure?
Here are the key factors to be considered when selecting the right project management structure for an organization:
- Project Complexity: Determine the level of project complexity and the need for cross-functional expertise.
- Team Member Specialization: Evaluate the degree of skill specialization required for project success.
- Resource Availability: Assess the availability and cost of resources, including human and material resources.
- Organizational Culture: Recognize how the adopted project organizational structure aligns with the existing culture and whether it could support or hinder cultural objectives.
- Project Duration: The expected duration of the project can impact the suitability of different structures.
- Stakeholder Expectations: Understand the expectations of key stakeholders and how the chosen project management structure can meet those expectations.
How Does a Company’s Organizational Structure Impact Project Management?
The organizational structure of a company can significantly impact project management due to the varying degrees of autonomy, influence, and resource accessibility, as the may be different for organizational type.
FOR EXAMPLE:
- A company with a Strong Matrix structure may see projects executed with greater swiftness and flexibility, as project managers have the authority to make decisions without the need for extensive consultations.
- Organizations with a Weak Matrix structure may experience delays or conflicts caused by the overriding interests of functional departments, which could impede project progress.
Selecting an effective project management structure is pivotal to the success of any initiative. Engaging in comprehensive online project management courses can also enhance one’s ability to adapt to varied project organizational structures.
