What is Project Portfolio Management (PPM)?
Project Portfolio Management, or PPM, is a collection of programs and projects that support a specific business goal or objective of an organization. Project Portfolio Manager ensures that all projects and programs do not operate in silos but work together to achieve common goals and objectives of an organization. PPM measures project performance, costs, and benefits, as well as their projections. As a result, organizations can adapt their project portfolio in the most efficient way possible, considering all business areas. Let’s say our company is in the construction business and has several business units: retail, single-family residential, and multifamily residential. Collectively, the projects within all of these business units make up the portfolio, and their management is project portfolio management.
Project Portfolio Management – Quick Overview
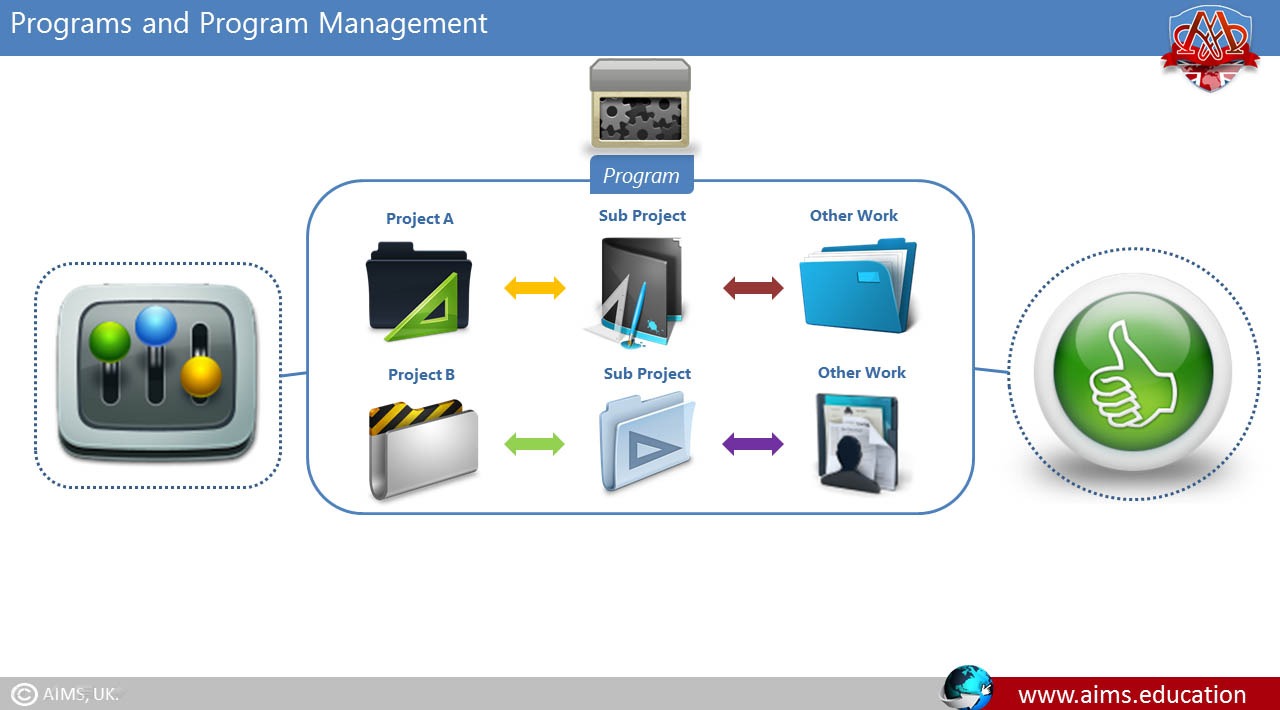
Project portfolios are collections of programs and projects that support a specific business goal or objective. The program management we discussed in the preceding section (the collection of projects associated with building the new shopping mall) is within our portfolio, but other programs and projects could also be within it. Programs and projects within a project portfolio are not necessarily related to one another directly. However, the overall objective of any program or project in this portfolio is to meet the strategic objectives of the portfolio, which in turn should meet the objectives of the department and, ultimately, the business unit or corporation.
Pacific Edge Software’s product manager, Eric Burke, defines project portfolio management as:
“The continuous process of selecting and managing the optimum set of project initiatives that deliver maximum business value.”
1. Role of a Portfolio Manager in Aligning Projects with Organizational Strategy
Managers responsible for Project Portfolio Management need to understand how projects fit into the organization’s bigger picture, especially in terms of corporate strategy, finances, and business risks. They create portfolios based on meeting specific organizational goals, such as maximizing the portfolio’s value or making effective use of limited resources. Portfolio managers help their organizations make wise investment decisions by helping to select and analyze projects from a strategic perspective. Portfolio managers may or may not have previous experience as project or program managers. It is most important that they have strong financial and analytical skills and understand how projects and programs can contribute to meeting strategic goals.
2. Understanding Project, Program, and Project Portfolio Management
The main distinction between project or program management and project portfolio management is a focus on meeting tactical versus strategic goals. Tactical goals are generally more specific and short-term than strategic goals, which emphasize long-term goals for an organization. Individual projects and programs often address tactical goals, whereas portfolio management addresses strategic goals.
3. Roles of a Project Portfolio Manager
Project and program management address questions like,
- Are we carrying out projects well?
- Are projects on time and on budget?
- Do project stakeholders know what they should be doing?
Project portfolio management addresses questions like,
- Are we working on the right projects?
- Are we investing in the right areas?
- Do we have the right resources to be competitive?
4. Examples of Project Portfolio Management
There can be portfolios for all types of projects. For example:
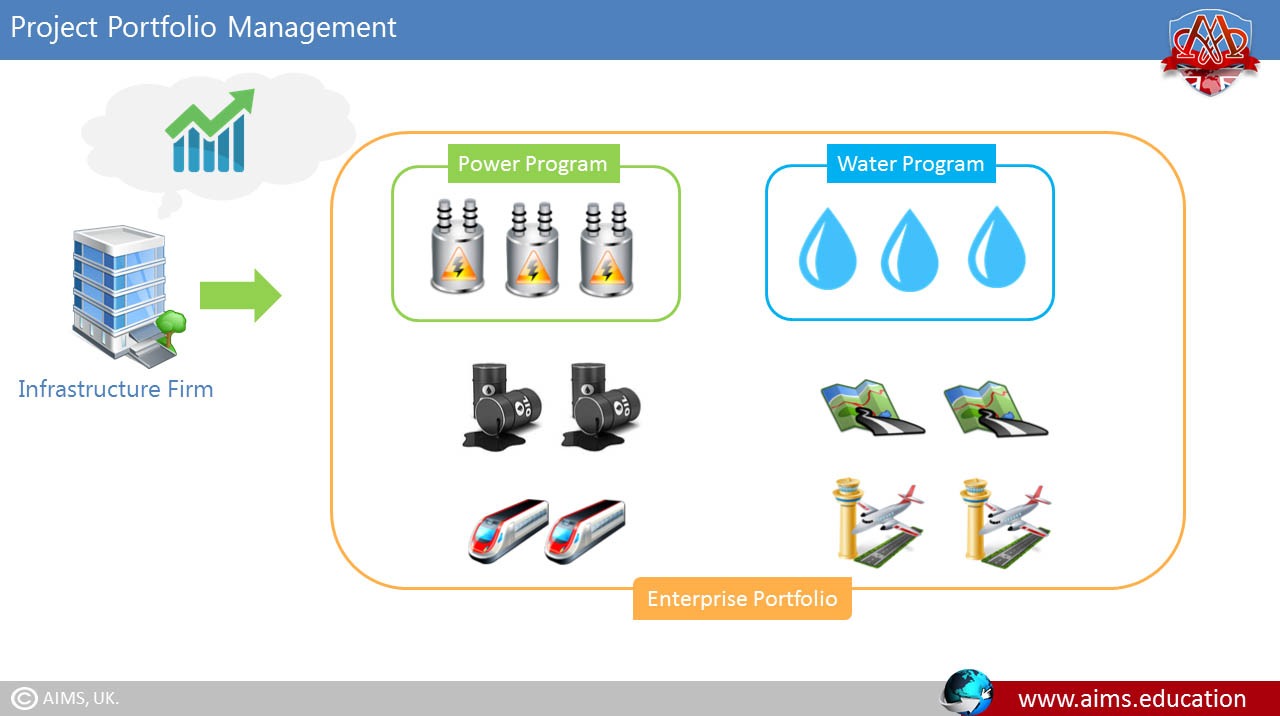
Example 1: Construction Firm
In a construction firm, strategic goals might include increasing profit margins on large projects, decreasing costs on supplies, and improving the skill levels of key workers. Projects could be grouped into these three categories for portfolio management purposes
Example 2: Clothing Firm
In a clothing firm, strategic goals might include improving the effectiveness of IT, introducing new clothing lines, reducing inventory costs, and increasing customer satisfaction. These might be the main categories for their portfolio of projects.
Example 3: Government Agency
A government agency for children’s services could group projects into a portfolio based on key strategies such as improving health, providing education, and so on to help make decisions on the best way to use available funds and resources.
“The main distinction between project or program management and project portfolio management is a focus on meeting tactical versus strategic goals. Tactical goals are generally more specific and short-term than strategic goals, which emphasize long-term goals for an organization. Individual projects and programs often address tactical goals, whereas portfolio management addresses strategic goals.”
Key Note!
Project Management VS Project Portfolio Management
PROJECT PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT | PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
| Focuses on a collection of projects and programs. | Focuses on the execution of a single project. |
| Aimed at strategic alignment with business goals. | Aimed at delivering specific outputs or deliverables. |
| Involves high-level resource allocation decisions. | Involves detailed resource scheduling and utilization for a project. |
| Requires prioritization based on business impact and risks. | Requires planning based on project scope, time, and cost. |
| Key decisions are driven by organizational strategy. | Key decisions are driven by project management objectives and constraints. |
| Manages dependencies between multiple projects. | Manages dependencies within the project tasks. |
| Emphasis on portfolio balance and value maximization. | Emphasis on successful project completion within constraints. |
| Addresses the overall risk of the portfolio. | Addresses risks specific to the project. |
| Monitored and measured by aggregated portfolio performance. | Monitored and measured by individual project success criteria. |
| Project Portfolio Management often involves a more dynamic and flexible approach to change. | Project Management often follows a structured methodology or framework. |
7 Key Roles of Project Portfolio Manager
Here are the seven key roles and responsibilities of a project portfolio management:
- Enhanced decision-making to comprehensive visibility into a portfolio.
- Resource optimization, cost savings and higher productivity.
- Strategic alignment to ensure that every project contributes to the overall business strategy.
- Risk management to identify and mitigate risks at the portfolio level.
- Performance measurement by evaluating projects collectively.
- Maintain an optimal balance in the project portfolio to stabilize returns.
- Improved delivery by applying the right project management methodologies.
3 Best Project Portfolio Management Software
Here are the three widely used project portfolio management tools:
1. Microsoft Project
Integrate seamlessly with the Microsoft ecosystem. Users benefit from advanced analytics and rich project and portfolio management functionalities.
2. Oracle’s Primavera P6
The Primavera P6 is ideal for large enterprises; it excels in handling complex, large-scale projects.
3. Planview
Planview features include strategic planning, portfolio and resource management, and enterprise architecture.
5 Best Project Portfolio Management Tools
1. Gantt Charts:
Creating Gantt charts provides a clear visual timeline of project schedules, dependencies, and progress.
2. Mind Mapping
Allos visual organization of ideas and tasks facilitates brainstorming, strategy planning, and the breakdown of large projects.
3. Project Dashboards
Dashboard functions help monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), such as portfolio health, project status, and milestones.
4. Resource Allocation Matrices
Allows allocation and utilization of workforce across multiple projects.
5. Kanban Boards
Help teams visualize workflow, prioritize tasks, and manage project progress in real time.
“To implement project portfolio management, you must first identify your organization’s objectives and goals. Once you’ve done this, create a project portfolio that aligns with these objectives and goals. Next, implement a Project Portfolio Management process that will help you track and manage your projects. Finally, use project portfolio management tools to improve its process.”
Key Note!
Project Portfolio Management Process Steps
The Project Portfolio Management (PPM) process typically involves several key steps to ensure a balanced portfolio that aligns with the organization’s strategic goals. The ten project portfolio management process steps are:
- Strategic Alignment.
- Initiation of Projects.
- Evaluation and Selection of Projects.
- Resource Allocation and Scheduling.
- Projects’ Execution and Control.
- Measurement of Performance.
- Portfolio Review and Rebalancing.
- Project Cost Management and Communications.
- Benefits Realization and Value Delivery.
- Lessons Learned and Continuous Improvement.
Key Component of Project Portfolio Management
The fundamental components of Project Portfolio Management (PPM) are as follows:
- Governance.
- Portfolio Evaluation.
- Resource Management.
- Performance Management.
- Benefits Realization.
- Risk Management.
- Stakeholder Engagement.
- Project Quality Management.
- Portfolio Reporting.

Examples of Processes and Techniques Used in Project Portfolio Management
Here are some of the processes and techniques used to ensure the effectiveness of Project Portfolio Management (PPM):
- Scenario Analysis.
- Risk Management.
- Resource Optimization.
- Project Change Management.
- Portfolio Scoring and Prioritization.
- Stakeholder Engagement.
- Earned Value Management (EVM).
Navigating Project Portfolios’ Complexity with Academic Expertise
Project portfolio manager plays a critical role, often backed by advanced education such as a Project Management PhD or a Post Graduate Diploma in Project Management. In recent years, the proliferation of online project management courses has further empowered professionals.
