What is PMO or Project Management Office?
PMO means Project Management Office, defined as “a management structure that standardizes the project-related governance processes and facilitates the sharing of resources, methodologies, tools, and techniques.” The functions of a PMO range from providing project management support to actually being responsible for the direct management of one or more projects. The PMOs are usually a centralized organizational unit that oversees the management of projects and programs throughout the organization.
Types and Functions of PMO
The most common reason a company starts PMO is to establish and maintain procedures and standards for the right project management methodologies and to manage resources assigned to the projects. After understanding the project management office definition, let us review its types. There are three types of Project Management Office functions in an organization, each varying in the degree of control and influence they have on projects within the organization. They are discussed below:
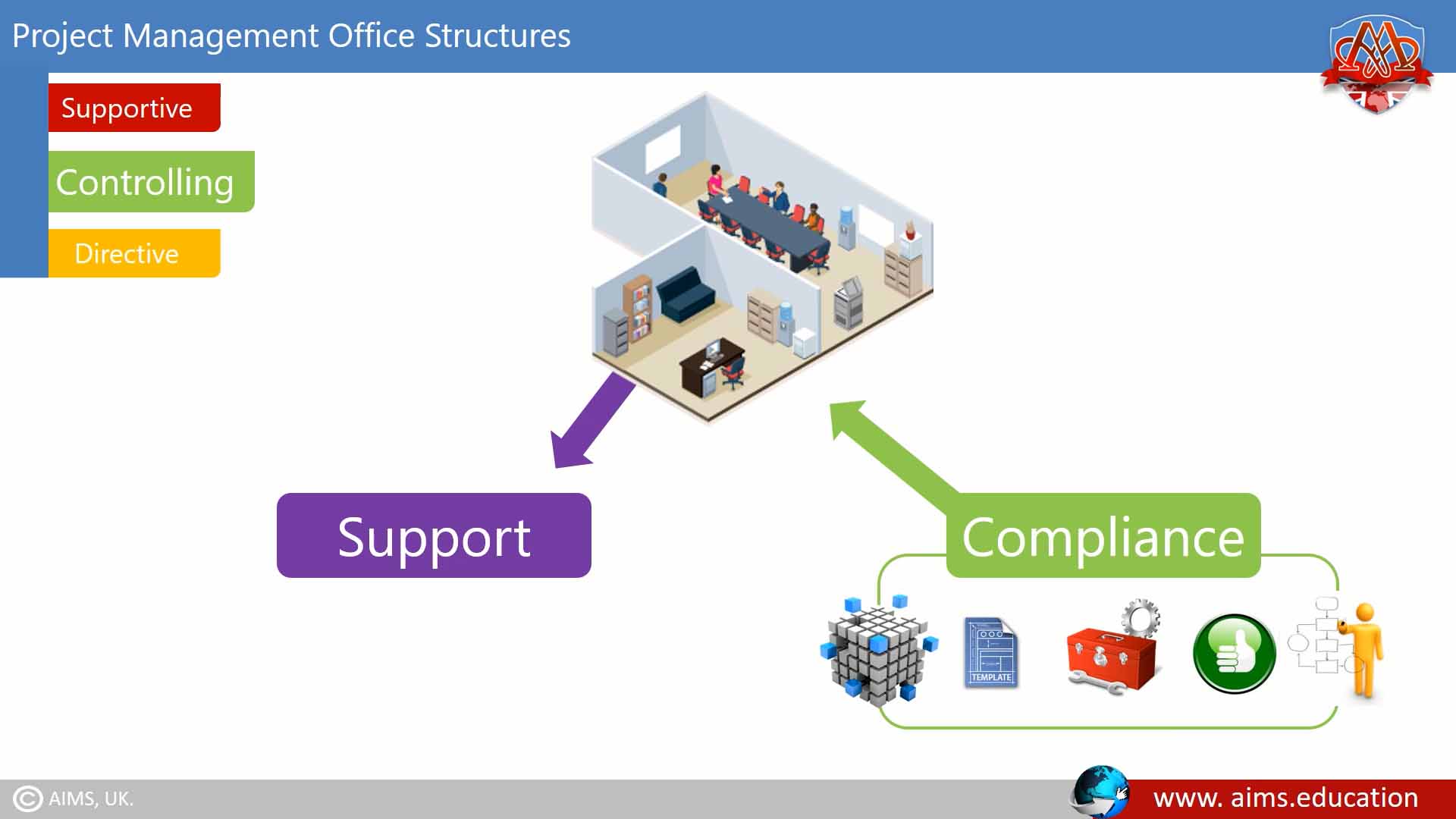
1. Supportive
It provides a consultative role to projects by supplying templates, best practices, training, access to information and lessons learned from other projects. It serves as a project repository. The degree of control provided is low.
2. Controlling
It provides support and requires compliance through various means. Compliance may involve adopting the project management frameworks or methodologies, using specific templates, forms, and tools, or conformance to governance. And it is based on the project management principles. The degree of control provided is moderate.
3. Directive
It takes control of the projects by directly managing projects. The degree of control provided by the directive project management office is high.
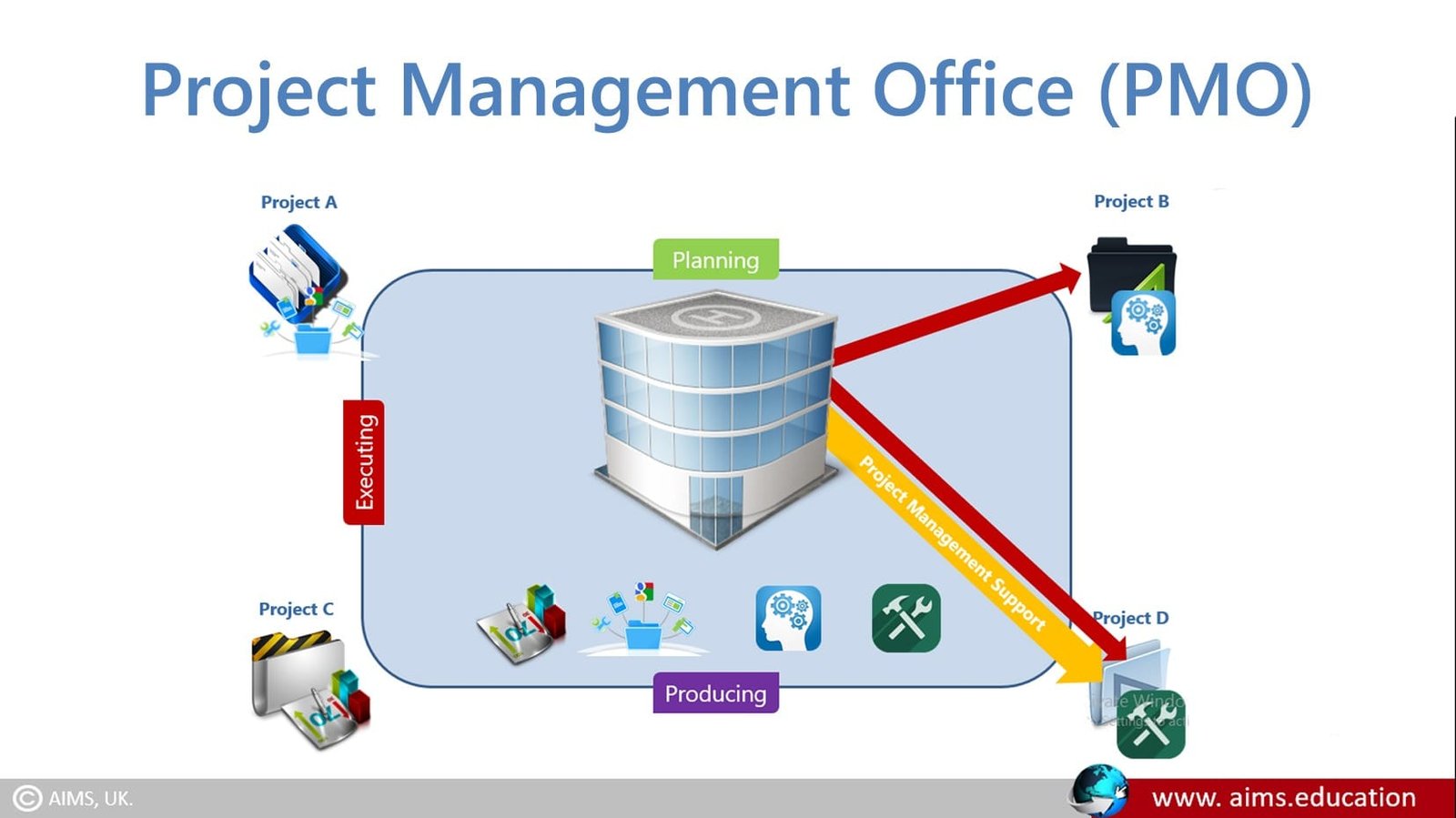
Role and Structure of a Project Management Office
The projects supported or administered may not be related other than by being managed together. The specific form, function, and structure of a project management office depend upon the needs of the organization it supports. It may have the authority to act as an integral stakeholder and a key decision-maker throughout each project’s life, make recommendations, terminate projects, or take other actions, as required, to remain aligned with the business objectives. In addition, the it may be involved in selecting, managing, and deploying shared or dedicated project time management and resources.
How PMO Supports Project Managers, Program Managers, and Project Portfolio Managers
They support project management, program management, and project portfolio management in a variety of ways, which may include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Managing shared resources across all projects within the office;
- Identifying and developing project management methodology, best practices, and standards;
- Coaching, mentoring, training, and oversight;
- Monitoring compliance with project management standards, policies, procedures, and templates by means of project audits;
- Developing and managing project policies, procedures, templates, and other shared documentation (organizational process assets); and
- Coordinating communication across projects.
PMO VS Project Manager
While both play crucial roles in project execution, their functions and responsibilities differ significantly.
Project Manager | Project Management Office | |
Scope of Responsibilities | Project Manager manages individual projects. | Oversees all projects within the organization. |
Degree of Authority | Holds direct control and decision-making power over single projects. | Make decisions that affect the entire portfolio of projects. |
Strategic Influence | Focused on solving day-to-day project issues. | A strategic role aligns all projects with organizational goals. |

What are Effective and Ineffective PMOs?
Let us look at the strengths and weaknesses of both the Effective and Ineffective:
Effective | Ineffective |
| Exhibit strong leadership. | Lack of a distinctive purpose. |
| Implement standardized methodologies for project management. | Absence of standardized project management procedures. |
| Proficient in project success. | Display a rigidity to adopt new business conditions. |
| Utilize advanced software and informed decision-making. | Struggle with inefficient practices that lead to project setbacks. |
| Champion a culture of continual learning and effective problem-solving. | Show resistance to change, so fail to meet project demands. |
Key Roles & Responsibilities of a PMO
Their key roles and responsibilities are as under:
- Strategic Planning,
- Governance,
- Resource Allocation,
- Training and Mentoring,
- Performance Tracking and Reporting,
- Risk Management, and,
- Project Quality Assurance.
Advance Your Project Management Career
- Diploma in project management provides advanced knowledge and skills, required to manage projects, programs and project portfolios.
- For those seeking a more higher managerial positions, an MBA in project management is a preferred choice for them.
- AIMS’ project management certification course or PMP training affirms professional’s competence in managing projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is a Project Management Office (PMO)?
A PMO is a centralized function that standardizes governance, methods, tools, and resource sharing across projects, often called a program management office.
Q2: What is PMO meaning versus PMO definition?
PMO meaning emphasizes its role in delivery support, while a formal PMO definition describes the structure that standardizes governance and facilitates shared methodologies.
Q3: What are the three main types of PMO?
Supportive (low control), Controlling (moderate compliance), and Directive (high control through direct project management).
Q4: How does a PMO support project management?
By managing shared resources, creating standards, training and mentoring, auditing compliance, and coordinating communication across projects.
Q5: PMO vs Project Manager—what’s the difference?
A Project Manager runs a single project day to day; a PMO oversees multiple projects, sets standards, and steers portfolio alignment.
Q6: When should an organization establish a PMO?
When multiple initiatives require consistent methods, shared resources, better governance, or portfolio-level visibility.
Q7: What characterizes an effective PMO?
Strong leadership, standardized methodologies, evidence-based decision-making, and a culture of continuous learning.
Q8: What are signs of an ineffective PMO?
Unclear purpose, no standard procedures, rigidity to change, and inefficient practices that hinder delivery.
Q9: How does a PMO help program management office work?
It aligns related projects to strategy, supports governance and resource planning, and standardizes reporting across programs.
Q10: Which responsibilities typically sit with a PMO?
Strategic planning, governance, resource allocation, training, performance tracking, risk management, and quality assurance.
Q11: How does a PMO improve cross-project communication?
By acting as the hub for status reporting, standards, and knowledge sharing, ensuring consistent information to stakeholders.
Q12: What is “pmo project management” in simple terms?
It’s the way a project management office structures practices, enforces methodologies, and supports teams to improve outcomes.
