What is WBS in Project Management?
Work Breakdown Structure or WBS project management is a process of breaking large projects into smaller tasks step by step, which makes the project work more approachable and ensures that the outcomes are productive and according to the project scope. The project manager creates the project management WBS by breaking down major deliverables into smaller systems and sub-deliverables, further decomposing them until specific work packages are identified. Each work package must be unique, and the sum of all packages should cover 100% of the project scope.
The WBS in project management is the foundation for calculating activities, resources, costs, and other aspects, facilitating effective project management. It is usually used for large, complex, and unique projects when the project scope is ambiguous.
7 Key Benefits of Work Breakdown Strcuture in Project Management
There are several benefits of breaking down a large project into smaller tasks. These benefits make it easier to visualize the project and tackle the project tasks separately rather than facing an overwhelming, undefined project task all at once. The WBS project management assists project managers to:
- Establish project management dependencies.
- Evaluate a project management timeline and make a schedule.
- Estimate the project management cost.
- Draft a statement of project work.
- Clarify the roles and responsibilities of the project manager and the people working on the project.
- Monitor the project’s progress.
- Recognize the risks related to the project.
3 Types of WBS Project Management
There are three types of WBS in project management, and they are: Deliverable-Based, Phase-Based, and Responsibility-Based. Each type differs in how the first level of the project management WBS is structured.
1. Deliverable-Based WBS
This project management WBS outlines the connection between the project’s deliverables (like products or services) and scope of the project. It breaks down the project scope into control accounts, which are further subdivided into work packages and tasks.
2. Phase-Based WBS
This type of WBS in project management divides the project into five key project management phases (initiation, planning, execution, control, and closeout) and identifies the deliverables within each phase.
3. Responsibility-Based WBS
This type of work breakdown structure in project management organizes project activities by the teams or organizational units responsible and outlines their tasks and roles. This type of project management WBS ensures that tasks are completed effectively by the designated teams.
WBS project management is an essential part of educational programs offered by AIMS’ institute of project management. These programs include the Certified Project Management certification, online diploma of project management, Masters degree in project management online.
9 Key Elements of a Project Management WBS
A good project management WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) typically includes:
- Clear hierarchy,
- Well-defined deliverables and
- Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable components.
These elements should be aligned with the project and project management objectives, and all work should be accounted for. Below are the nine key elements of a WBS in project management:
1. Phases
These are the major stages of the project life cycle, grouping related activities and tasks.
2. Tasks
Tasks are the specific activities performed within each project phase.
3. Subtasks
Smaller components of tasks, enabling detailed planning and execution.
4. Deliverables
Outputs, either tangible or intangible, are produced upon task completion.
5. Sub-Deliverables
These are the smaller outputs that contribute to achieving larger deliverables.
6. Work Packages
The smallest units in a WBS consist of detailed tasks with specific deliverables.
7. Dependencies
Relationships between tasks indicate which must be completed first.
8. Estimates
These are the approximations of resources, time, and costs to budget and schedule the project.
9. Milestones
Milestones are the key points marking the completion of important phases or goals within the project.
How to Implement WBS Project Management?
Below are the six key steps, that are used to effectively implement a WBS in project management:
Step-1: Define Project Scope and Objectives
This step clearly outlines the project’s goals, constraints, and requirements, and form a solid foundation for the WBS.
Step-2: Identify Major Deliverables
Here, the project manager list the primary outputs – that the project aims to achieve. Examples of these deliverables are UI design, backend development, or database setup for a mobile application project.
Step-3: Break down Deliverables
Here, the project managers divide major deliverables into smaller sub-deliverables, for example, wireframes, mockups, and design reviews for UI.
Step-4: Identify Work Packages
Break sub-deliverables into specific work packages, like sketching, reviewing, and finalizing wireframes.
Step-5: Define Activities
This step details the tasks, resources, and dependencies for each work package, e.g., gathering requirements and creating initial sketches.
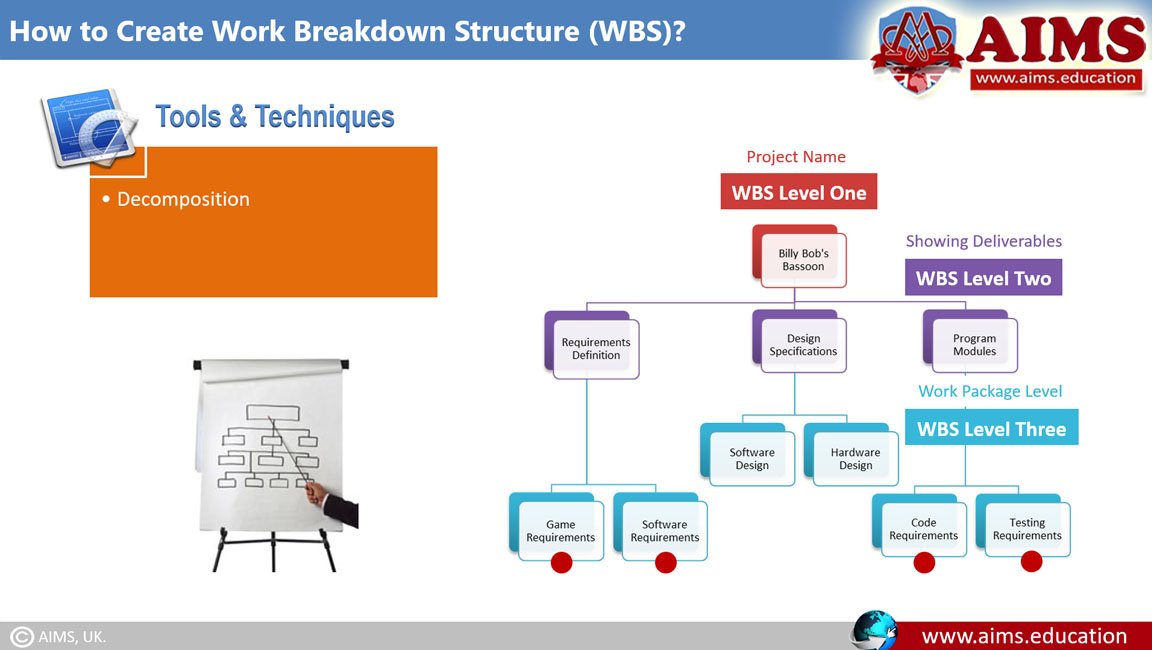
Step-6: Create a WBS Chart
Finally, in the WBS project management process, the project managers organize the WBS into a visual hierarchy, from the overall project to individual tasks, using a tool (for example, a Gantt chart).
3 Key Rules to Prepare an Effective WBS in Project Management
Project managers must follow the following three rules to create an effective work breakdown structure in project management:
Rule 1: The 100% Rule
Your WBS in project management should include 100% of the work needed to achieve the overall project goal, excluding any unrelated tasks. Each child task must cover all the work required to complete its parent task.
Rule 2: Mutually Exclusive
Avoid duplicating sub-tasks or work in your project management WBS, as it violates the above-mentioned 100% rule and can lead to resource miscalculations.
Rule 3: Outcomes, Not Actions
Focus on deliverables and outcomes, not actions. For example, a deliverable might be “the braking system,” while an action would be “calibrates the brake pads.”
5 Tools to Implement WBS in Project Management
1. Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart is a visual tool for WBS project management that illustrates the project life cycle by displaying tasks along a timeline. It highlights timeframes, dependencies, and progress. Gantt Chart is an effective tool for teams needing clear guidance on the project schedule. Combining this WBS project management tool enhances the planning and scheduling capabilities of a project.
2. Kanban Boards
Kanban is a visual approach to managing project tasks as they progress through various stages. It uses cards on Kanban boards to represent tasks, with columns showing different workflow phases. This method is particularly suited for projects following the agile project management methodology, and it involves ongoing monitoring and regular adjustments.
3. Calendars
Calendars in project management offer a time-based framework for the WBS, ensuring tasks are completed within defined time frames. Calendars also help track deadlines, milestones, and resource availability. This approach is most effective for projects with strict deadlines or fixed schedules.
4. WBS Family Tree Hierarchy
This tool’s work breakdowns should follow a logical, hierarchical structure resembling a family tree. This systematic approach is why the term “work breakdown structure” (WBS) is widely used.
5. Logical Interfacing and Completeness
A work breakdown can also be seen as a jigsaw puzzle, where every piece fits perfectly, and none is missing. This WBS visualization is helpful for ensuring completeness and proper organization. In this project management WBS tool:
- Each puzzle piece must be clearly identified and placed using a logical numbering system, where each piece serves as its locator or address.
- It must be ensured that nothing is missing, and here, the checklists can help minimize the risk of omissions.
WBS Project Management Example
Suppose you have to manage a complex mining or processing plant project for on-site extraction of mineral resources in a previously uninhabited area far from the nearest railhead, port, or airport. While constructing the plant might cost hundreds of millions of pounds, it would only be one part of the overall project. Additional infrastructure, such as roads, railways, an airstrip, housing, schools, churches, hospitals, shops, and even an entire township, might also need to be developed.
Now you need to perform the following tasks:
- Estimate the cost of such a large project,
- Set budgets and,
- Make plans to manage the project work.
So, your project is too complex, and it is not possible for you to estimate, plan, and control it effectively without first breaking it into smaller sub-projects.
- These subprojects must then be further divided into manageable work packages and tasks.
- The work breakdown structure for a large mining project highlights the major work packages identified at the initial stages.
So in practice, “the WBS project management process would continue, and you will have to divide the work into smaller packages until it reaches the individual tasks and purchases at the lowest level”.
WBS Complementary Structures
The following three structures complement the WBS in project management by focusing on resources, risks, and organizational roles. These structures ensure that the project is well-managed from all angles.
1. Resource Breakdown Structure
It is a project management structure that offers a hierarchical breakdown of resources organized by resource type, category, or function.
2. Risk Breakdown Structure
A Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS) is a hierarchical framework that decomposes risks, beginning with the root element and branching out into various risk categories.
3. Organizational Breakdown Structure
Also referred to as an Organizational Chart, the Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS) represents the project’s organizational structure. It typically starts with the project sponsor and includes all key stakeholders.
Key Takeaways
- A WBS project management is an effective management tool for ensuring project success.
- The project management WBS is utilized by various groups for different purposes.
- There are three types of WBS in project management: Deliverable-Based, Phase-Based, and Responsibility Based.
- WBS project management can be created using numerous online tools, such as Gantt Chart, Kanban Boards, Calendars, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is WBS in project management?
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) decomposes a large project into smaller, manageable deliverables and work packages so teams can plan, estimate, assign responsibilities, and control scope effectively.
Q2: How does a WBS support project planning and control?
By structuring deliverables into work packages, the WBS enables accurate estimates of cost, time, and resources, clarifies roles, highlights dependencies, and provides a baseline to schedule, track progress, and manage risks.
Q3: What are the three main types of WBS?
Deliverable-Based, Phase-Based, and Responsibility-Based—each organises the first level differently to match outputs, life-cycle phases, or accountable teams.
Q4: What are the key elements of a project management WBS?
Phases, tasks, subtasks, deliverables, sub-deliverables, work packages, dependencies, estimates, and milestones—arranged in a clear hierarchy tied to project objectives.
Q5: What is the 100% rule in WBS project management?
The WBS must capture 100% of the scope. Each child element fully represents the work required to complete its parent, without unrelated tasks or omissions.
Q6: How do you implement a WBS step by step?
Define scope and objectives, identify major deliverables, decompose into sub-deliverables, define work packages, specify activities with resources and dependencies, then organise everything into a visual WBS chart.
Q7: What tools help build or use a WBS?
Gantt charts, Kanban boards, calendars, a hierarchical WBS tree, and completeness checklists support planning, scheduling, and quality control.
Q8: What’s the difference between deliverables and actions in a WBS?
A WBS is outcome-driven. “Braking system” is a deliverable; “calibrate brake pads” is an action. Focusing on deliverables prevents scope drift.
Q9: When should you use a Responsibility-Based WBS?
When ownership and handoffs must be explicit. Group work by teams or organisational units for clearer accountability and coordination.
Q10: How does WBS relate to resource, risk, and organisational structures?
Use RBS for resources, RBS (risk) for threats and categories, and OBS for roles and reporting. Together they complement the scope focus of the WBS.
Q11: Can you give an example of WBS project management in practice?
A mining megaproject can be decomposed into plant, infrastructure, and community subprojects, then into work packages until lowest-level tasks and purchases are defined.
Q12: What common mistakes should be avoided when creating a WBS?
Duplicating scope, mixing actions with deliverables, weak hierarchy, missing the 100% rule, and poorly defined work packages that undermine estimating and tracking.
