What is Scrum Project Management?
A project’s ultimate success or failure depends on how they are managed and led. So, to ensure that your project is a success, you need to find the right project management method. One of the most popular methods used is scrum. Scrum project management is an agile methodology that helps teams deliver high-quality products in the shortest amount of time while continuously adapting to change. The scrum project management approach involves collaborating with a cross-functional team, working in short iterations known as sprints, and following a set of predefined roles, ceremonies, and artifacts. This framework enables teams to deliver the most valuable features first and allows for continuous improvement and customer feedback.
What are Sprints in Scrum Project Management?
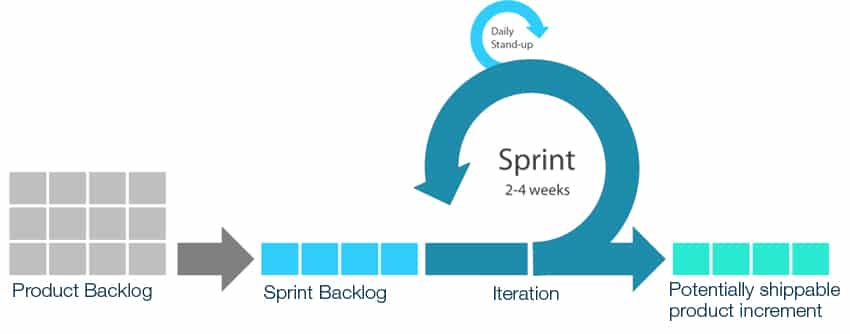
A sprint, in scrum project management, is a set period during which specific work must be completed and made ready for review. Each sprint begins with a planning meeting. During the meeting, the product owner (the person requesting the work) and the development team agree upon exactly what work will be accomplished during the sprint.
How Do Sprints Relate to Scrum?
Scrum and sprints go hand in hand to provide an effective project management approach. The scrum project management methodology provides the framework for managing projects, while sprints allow for the actual work to be completed in short cycles.
- Sprints are time-boxed events of one month or less that serve as a container for the other Scrum events of Planning, Daily Scrum, Review, and Retrospective.
- They are the primary vehicle used in Scrum to inspect progress and adapt plans accordingly, ensuring continuous improvement in terms of quality and efficiency.
- Additionally, sprints promote a level of transparency as each member of the team knows what’s expected and what deliverables must be completed by the end of the sprint.
Scrum VS. Sprint in Project Management:
Scrum and sprint, while closely related in the realm of project management, have distinct roles and characteristics. Here are the key differences:
| Scrum VS. Sprint: What’s the Difference? | |
|---|---|
| Scrum project management is a methodology or framework. It embodies an iterative and incremental approach. | Sprint is a specific time-boxed period integral to the Scrum framework where certain milestones or tasks must be accomplished. |
| Scrum is applied to the entire project. It encompasses specific roles, meetings, and outputs, in which sprints play a key part. | Sprint refers to the individual iterations within the project, each with a defined duration and goal. |
| Scrum’s primary objective is to enhance team productivity, foster collaboration, and deliver high-quality products promptly. | Sprint’s purpose is to break the project into manageable chunks, allowing for regular reviews, adjustments, and progress tracking. |
| Scrum project management is a consistent approach throughout a project’s lifecycle. | Sprints are discrete, repetitive elements that occur multiple times within the Scrum framework. |
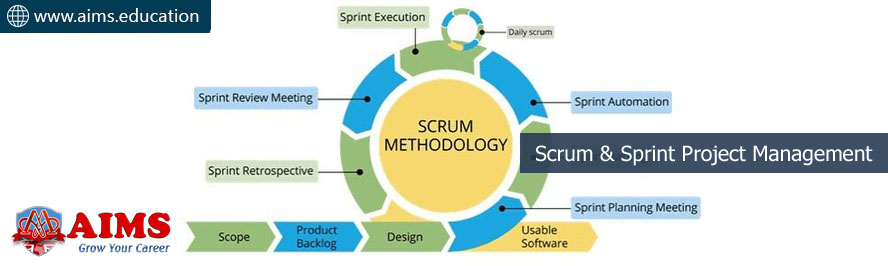
4 Stages of a Scrum Sprint Process:
The Scrum Sprint process is divided into four key stages:
Stage 1: SPRINT PLANNING
This is the inaugural stage where the Scrum project management team collaboratively decides on the work that will be accomplished during the sprint. The Product Owner presents the highest priority items from the product backlog, and the team cohesively determines how many of these items they can complete within the sprint duration.
Stage 2: SPRINT EXECUTION
After planning, the team commences work on the defined tasks. The focus is on task completion, fostering a productive, creative, and focused environment. Daily stand-up meetings or ‘Daily Scrum’ are conducted to monitor progress and address any potential issues promptly.
Stage 3: SPRINT REVIEW
This is the assessment phase at the end of the sprint where the team presents the completed work to the stakeholders. Feedback is collected, changes are suggested, and any incomplete tasks are returned to the product backlog for inclusion in future sprints.
Stage 4: SPRINT RETROSPECTIVE
The final stage of scrum project management involves the team reflecting on the completed sprint. The focus is on continuous improvement, with the team discussing what went well, what could be improved, and how to implement potential enhancements in future sprints. This stage confirms the Scrum project management methodology’s commitment to incremental, iterative progress.
1. How to Start your Scrum Sprint Planning?
Effective Scrum sprint planning sets the foundation for a successful sprint. Initiating your Scrum sprint planning involves a few crucial steps:
A. PRODUCT BACKLOG REFINEMENT:
Before you start your sprint planning, make sure your product backlog is prioritized and up-to-date. In scurm project management, the Product Owner should have a clear understanding of what the business needs and which items hold the highest value.
B. SCRUM TEAM AVAILABILITY:
Check the availability of your Scrum team. Holidays, vacations, or other commitments can impact the amount of work that can be taken on during the sprint. Having this information at hand will assist in avoiding overloading the team.
C. ESTABLISH THE SPRINT GOAL:
The Product Owner, in collaboration with the Scrum team, should establish a clear and concise sprint goal. This provides direction and focus, helping the team understand the context and purpose of their upcoming work.
D. CAPACITY PLANNING:
Based on the team’s availability and the complexity of the tasks, determine the team’s capacity for the upcoming sprint. This will guide the scrum project management team to understand how much work they can commit to.
E. SPRINT BACKLOG CREATION:
Finally, the team collaboratively selects items from the product backlog to include in the sprint backlog. These are the tasks that the team commits to complete during the upcoming sprint. The sprint backlog is a reflection of the team’s commitment to achieving the sprint goal.
2. How to Implement the Scrum Project Management Framework?
Implementing the Scrum project management framework is a cooperative process that requires clear understanding and commitment from the entire project team. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Understand the Scrum Principles: The first step is to gain a comprehensive understanding of Scrum principles, including its roles, artifacts, and events.
- Assemble the Scrum Team: The scrum project management team typically consists of a Product Owner, a Scrum Master, and the Development Team. Each member has distinct roles and responsibilities that contribute to the project’s success.
- Create the Product Backlog: The Product Owner develops a product backlog, a prioritized list of features, functions, requirements, enhancements, and fixes for the product.
- Plan the Sprint: The team then plans the sprint, determining which items from the product backlog to work on during the sprint.
- Execute the Sprint: The project management team works on the tasks decided in the sprint planning, with daily Scrum meetings to track progress and address any issues.
- Review the Sprint: At the end of the sprint, the team reviews the work accomplished and adjusts the product backlog if necessary.
- Retrospective Meeting: The team holds a retrospective meeting to discuss what went well, what didn’t, and how they can improve for the next sprint.
Remember, Scrum project management is an ongoing, iterative process. Each cycle brings a product increment, bringing the project closer to its final goal. Scrum thrives on transparency, inspection, and adaptation, making it a powerful tool in sprint project management.
3. Gaining Expertise in Scrum and Sprint Project Management
Enhancing your knowledge and expertise in scrum project management and sprint project management can be achieved through various qualifications and certifications. In the UK, project management qualifications are highly valued, providing a solid foundation in the field. The CPM certificate is a globally recognized credential that verifies your ability to manage complex projects effectively using scrum project management methodology. Similarly, obtaining a project management certificate, or even a diploma of project management, can further validate your skills and experience. For those willing to invest more time and effort, pursuing an MBA online in Project Management or a PhD in project management in the UK can open doors to senior roles in the industry. These advanced degrees typically cover in-depth study of project sprints, scrum in project management, and other advanced project management topics.
4. Benefits of Scrum Project Management:
1. Everyone Knows What To Do All The Time:
Team members know exactly what to do and any question can be answered immediately during the next sprint.
2. Easy Integration Of Feedback From Customers:
Since scrum project management is flexible and agile, you can easily incorporate feedback from customers at any point.
3. Smaller Tasks:
Most projects tend to include big tasks that are difficult to complete. When you use scrum project management, you can divide these into smaller tasks that are not only easier to manage but also to complete.
4. Continuous Testing:
No matter what you are producing, you can test it during the creation phase.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of Sprint Project Management:
- One of the major advantages of using sprint project management is that it allows organizations to stay on track with their projects. Another advantage is that it helps organizations to meet deadlines.
- One of the main disadvantages of sprint project management is that it requires a lot of time and effort. This can become an obstacle for small businesses with limited resources.
Sprint project management can be used in different types of projects such as marketing campaigns, software development projects, product launches, and other similar initiatives.
6. Applications of Scrum Projects:
Scrum project management is an agile methodology for project management that has been proven to be effective in a wide variety of industries. Scrum project management can be effectively utilized in a variety of fields.
EXAMPLE # 1: Software Development:
A tech company is working on a new mobile application. Scrum enables the team to address complex adaptive problems while delivering valuable products iteratively and incrementally. They organize their work into a backlog, prioritize tasks, and work in 2-week sprints, showcasing progress at the end of each cycle to stakeholders.
EXAMPLE # 2: Marketing Campaigns:
A marketing team at a retail company is launching a new product line. They use Scrum to collaborate dynamically on campaign elements like advertisement design, copywriting, and multimedia content. By working in short sprints and having daily stand-up meetings, they can quickly adapt to market responses and iterate their strategy for maximum impact.
Wrapping Up:
In conclusion, scrum project management and sprints are valuable tools for successful project management. By following the principles of transparency, inspection, and adaptation, teams can deliver high-quality products in a timely and efficient manner. The flexibility and collaboration fostered by this methodology make it a popular choice for project management in various industries. As the agile approach in project management continues to gain popularity, professionals in project management must familiarize themselves with scrum and sprints and their benefits. So, it can be said that Scrum and Sprint are two powerful tools that have revolutionized project management and helped businesses achieve their goals more effectively.
