Murabaha Meaning:
Murabaha “مرابحة” is a contract wherein the Islamic Bank, upon request by the customer, purchases the asset from a third-party supplier/vendor and resells it to the customer either against immediate payment or on a deferred payment basis. Al Murabahah means “cost plus financing,” derived from the Arabic word Rabah, which means “profit.” Murabaha contract is the sale of goods at cost plus an agreed profit.
How Does Murabaha Work?
Murabaha in Islamic banking progresses through four stages:
- Promise Stage,
- Agency Stage,
- Acquiring Possession, and,
- Execution.
1. Promise Stage
The transaction parties must be genuine. The nature of the business must be within the scope of Murabahah and should be Halal as well. Deferred payment is not permissible in the case of Gold, Silver, and Currencies; however, after this consideration, the limit may be approved. After Credit approval, the Bank will sign the Murabaha Agreement, and the Islamic Shariah status of this agreement will be a promise MOU.

2. Agency Stage
The Client orders the institution to buy certain goods for him and sell them after acquiring them. The prerequisite is that the goods are not already owned by the client. At this stage of the Murabaha contract, the customer promises the institution to buy the goods that the institute acquired at his request.
3. Acquiring Possession
Once the customer purchases the goods, the risk of the goods is transferred to the Islamic Bank. The Islamic Bank can now sell these goods to the customer. Note that the customer plays two different roles in this transaction. One is that of the bank’s agent, and the other is of the purchaser. These roles should be clearly segregated to make the transaction halal.
4. Acquisition of Title & Possession of the Asset
Institutions must take constructive or actual possession of the product being sold. And goods must exist at the time of execution of the Al Murabahah contract. The contract cannot be executed if the above two conditions are not fulfilled.

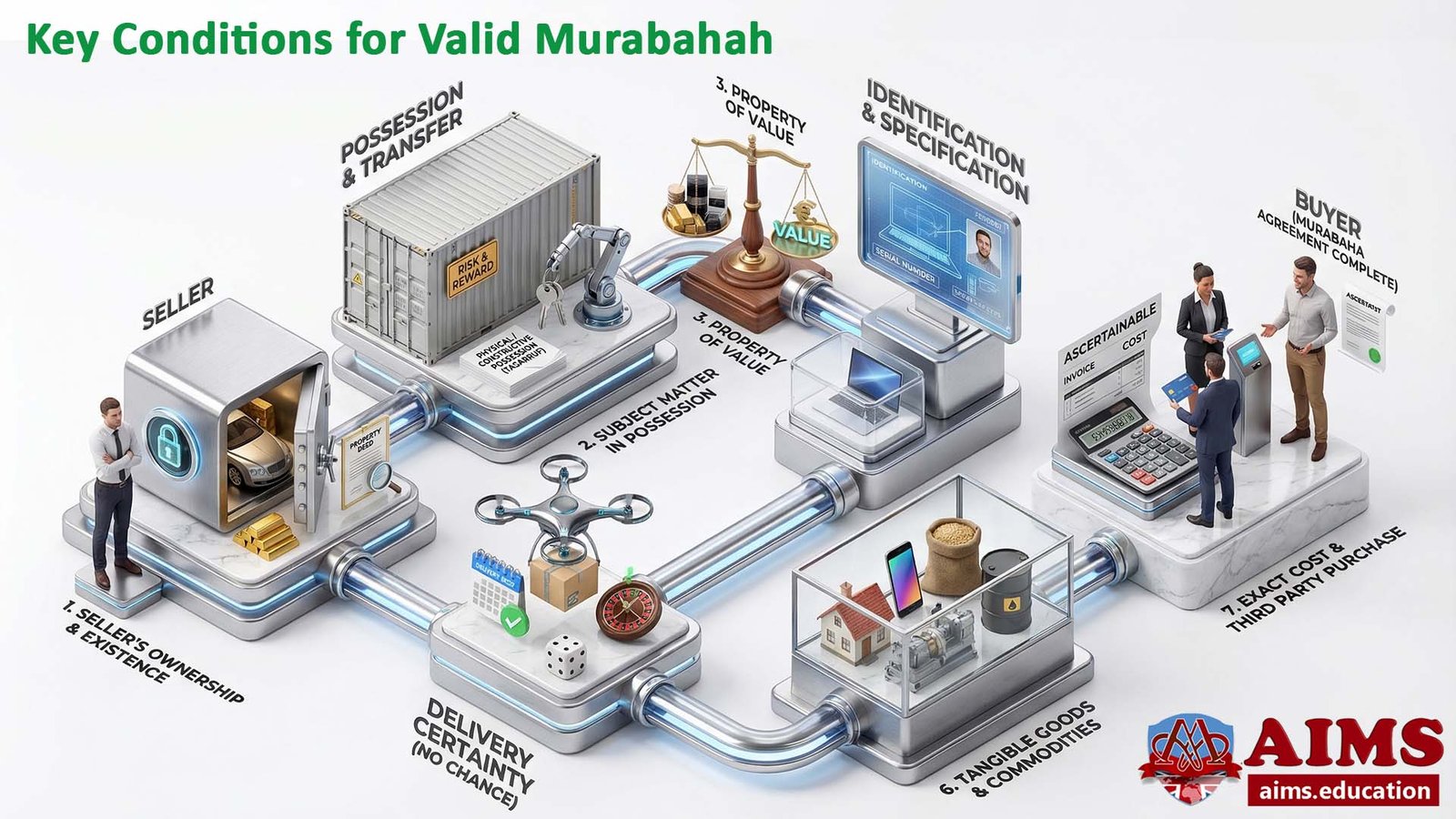
Basic Rules of Murabaha Agreement
1. Conditions of Subject Matter:
- The item must exist and must be in the seller’s ownership.
- Subject Matter must be in the physical or constructive possession of the seller (transfer of risk and reward and permission of use/Tasarruf).
- The subject of sale must be a property of value. The subject of the contract should not be a thing that is not used except for haram purposes.
- The subject matter must be specifically known and identified to the buyer.
- The delivery of subject matter must be certain and should not depend on chance.
- The subject matter must be tangible goods and commodities.
- The exact cost of the subject matter can be ascertained, and a third party purchases it.
2. Conditional Sale:
There are four types of conditions:
- A condition which is the requirement of sale (Valid).
- Reasonable condition for the safety of Subject matter (Valid).
- Unreasonable condition but in accordance with normal market practice (Valid).
- Condition which is Against the requirement of sale, Not in accordance with the market practice Beneficial for the seller or purchaser (void).
Pricing in Murabahah
The price must be certain (lump sum/by percentage). It may be deferred or on the spot, and if it is deferred, the instalments and due date must be determined. When the price is fixed, it cannot be decreased in case of earlier payment, whereas it cannot be increased in case of default. Fluctuation in the price is not permissible. However, the use of a benchmark at the time of the Master Financing Agreement is permissible.
Expenses of Murabaha
The expenses incurred by the seller directly in acquiring the commodity, such as freight and customs duty, can be included in the cost price.
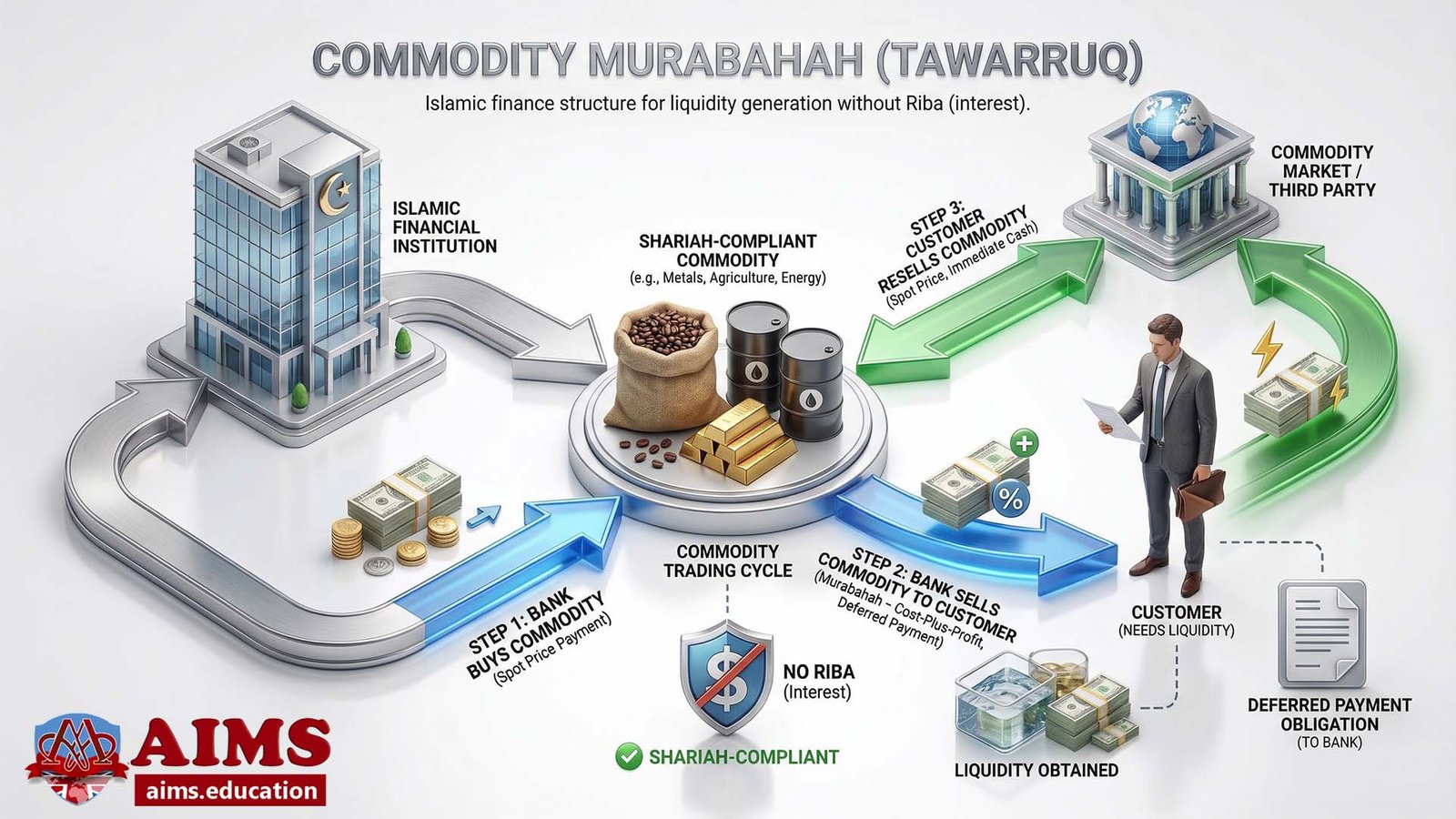
What is Commodity Murabahah?
Commodity Murabaha is the type that includes these different contracts:
- Master financing agreement between bank and customer.
- Undertaking from the client.
- Agency agreement between bank and customer.
- Purchase of goods from the supplier.
- Agreement between bank and client.
One must follow the sequence in agreements, and maintaining the sequence between 3, 4, and 5 is especially important.
The mechanism of Al Murabahah Financial Contract, its accounting standards, AAOIFI Shariah standards, design, and real-world application are part of AIMS’ globally accredited Islamic banking certification and MBA in Islamic Finance degree programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is Murabaha in Islamic banking?
Murabaha is a cost-plus sale where the bank buys a specified asset and resells it to the client at cost plus an agreed profit, with price and costs disclosed.
Q2: How does a Murabaha contract work step by step?
Promise, agency, bank acquisition of title/possession (bearing risk), then execution as a disclosed cost-plus sale on spot or deferred terms.
Q3: What is the Murabaha meaning and definition?
It means selling at cost plus a known profit, emphasising transparency of cost and profit and transfer of ownership upon sale.
Q4: When is Murabaha financing not permissible?
Not for deferred sales of gold, silver, or currencies. Goods must be halal, existing, owned, and possessed by the seller at execution.
Q5: What conditions apply to the subject matter?
The goods must exist, be valuable and halal, specifically identified, deliverable with certainty, and owned/possessed by the seller.
Q6: What are common types of Murabaha arrangements?
Commodity Murabaha with master agreement, client undertaking, agency, supplier purchase, and bank sale—keeping the proper sequence.
Q7: How are price and instalments set?
Price is fixed (lump sum or percentage). If deferred, instalments and due dates are specified; no increase for delay or discount for early payment.
Q8: Which expenses can be included in cost price?
Direct acquisition costs such as freight and customs duty incurred by the seller can be included in the disclosed cost.
Q9: What roles can the client play?
The client may act as the bank’s agent to procure goods, then as the purchaser; roles must be segregated and risk shifts to the bank on possession.
Q10: How does Murabaha differ from interest-based lending?
It is a sale of an asset at a disclosed cost plus profit, not a money loan; the bank bears ownership risk before resale.
Q11: What mistakes should be avoided?
Don’t sell before bank ownership, blur agency and purchaser roles, sell non-existent goods, or omit clear price and delivery terms.
Q12: What standards guide Murabaha practice?
AAOIFI Shariah and accounting standards—focusing on real asset ownership, risk transfer, sequencing, and transparent cost-plus disclosure.
