Islamic Banking VS Conventional Banking:
Banking, an essential facet of our daily lives, manifests in two primary forms: Islamic banking and conventional banking. These two systems differ substantially, as evidenced by their operating procedures and policies. The key difference between Islamic banking and conventional banking lies in their regulatory frameworks. Islamic banking operates under the strict guidelines of Sharia laws, unlike the conventional banking system. Notably, conventional banks may impose interest (Riba) and participate in the trade of items forbidden under Shariah, such as Alcohol and Pork, or engage in practices deemed uncertain (Gharar) or akin to gambling (Maysir). The ensuing segment provides a comprehensive comparative analysis of Islamic banking vs conventional banking, highlighting these differences in greater detail.

1. What is Conventional Banking:
A. CONVENTIONAL ACCOUNT MEANING:
To comprehend the difference between Islamic banking and conventional banking, one must first understand the conventional account meaning. Conventional banking is the traditional way of banking that involves taking deposits from individuals and businesses and making loans to those who need financing. This type of banking allows individuals to put their money into a conventional bank, where it can sit and earn interest while they are not using it. Individuals can also make small loans at this time, such as for a car or home improvement project.
B. TYPES OF CONVENTIONAL ACCOUNTS:
In conventional banking, there are three main types of products: savings accounts, checking accounts, and time deposits.
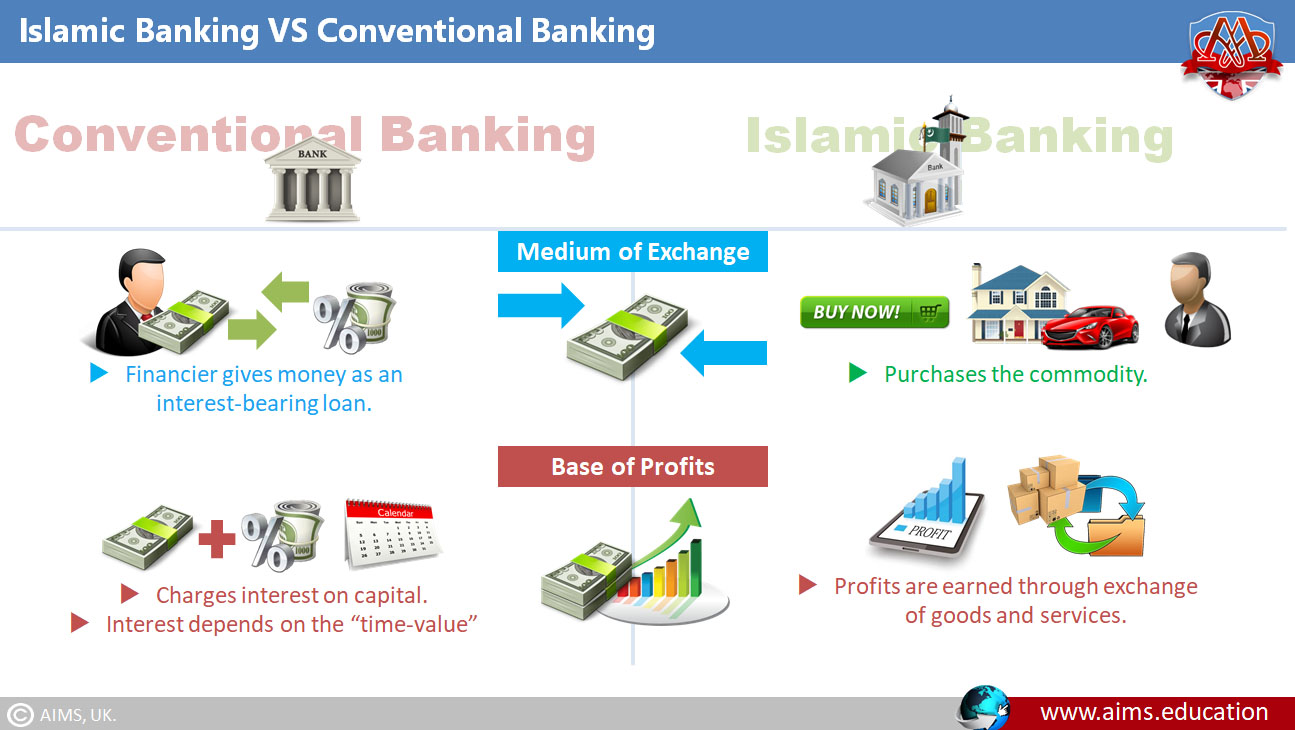
- Saving Accounts: These accounts allow people to store their money and earn interest (Riba) on it at the same time.
- Saving Account: Savings account allows clients to save their earnings and use them later when needed.
- Time Deposits: They are similar to checking accounts but with higher interest rates.
All these products are also found in Islamic banks but with the elimination of Interest (Riba) and other prohibited elements.
2. Islamic Banking:
A. DEEP DIVE INTO SHARIA LAW-BASED FINANCIAL SERVICES
Islamic banking is a type of finance that involves the use of profit-sharing, interest-free Islamic loans, and other financial services based on the principles of Islamic Sharia law. Unlike conventional banking, which charges interest on loans, Islamic banks are structured to encourage financial transactions with a principal focus on charity and community development.
B. ISLAMIC VS CONVENTIONAL BANKING: OPERATIONAL METHODOLOGIES
In many ways, Islamic banking is similar to conventional banking in that it allows individuals to save their money and receive loans for large purchases such as homes or vehicles. However, there are also differences in how Islamic banks operate. It’s often referred to as “ethical” or “people-friendly” banking. As well as being more ethical, Islamic banking is also more environmentally friendly than conventional banking because it encourages people to make smaller loans rather than take out large ones. In the context of sustainability, the difference between Islamic banking and conventional banking is notable, with Islamic financial institutions potentially having a more enduring model due to their unique principles and practices.
Islamic Banking VS Conventional Banking
“Islamic banking is an Ethical Banking System, and its practices are based on Islamic (Shariah) laws. Interest in completely prohibited in Islamic banking. It is asset based financing, in which trade of elements prohibited by Islam are not allowed. For example, you cannot take a loan for a Wine Shop. On the other hand, Conventional Banking is an Un-Ethical Banking system based on Man-Made Laws. It is profit-oriented and its purpose is to make money through interest”..
Key Note!

Difference between Islamic Banking and Conventional Banking:
Now, let us review some major differences between Islamic banking and conventional banking systems:
Conventional Banking System | Islamic Banking System |
INTEREST (RIBA) | |
| Conventional banks operate on traditional financial models including interest-based transactions. | Islamic banking is based on the principles of Islamic or Muslim law, which discourages usury (Riba) and promotes risk sharing. |
PROFIT AND LOSS SHARING | |
| The bank earns interest on loans and pays interest on deposits. | Profit and loss are shared between the bank and the customer. |
RISK SHARING | |
| The customer bears the risk. | Risk is shared between the bank and the customer. |
COMMUNITY WELFARE | |
| No such ethical restrictions are imposed. | Financial transactions must comply with ethical standards and contribute to the welfare of the community. |
INVESTMENT RESTRICTIONS | |
| There are no restrictions on the type of investment. | Investments in industries deemed Haram (forbidden) – including those related to alcohol, pork, and gambling or maisir, among others – are strictly disallowed. |
CREDIT BASE | |
| Often interacting with non-physical assets, conventional banking facilitates the generation of credit. | Islamic finance promotes asset-backed financing and encourages real Islamic economic activities. |
PRICING OF FINANCIAL PRODUCTS | |
| The pricing of financial products is often based on the prevailing market interest rate. | The determination of the cost for financial products is linked directly to an underpinning asset, commodity, or specified project. |
MONEY CLASS | |
| Money is a product besides a medium of exchange and a store of value. | Real Asset is a product. Money is just a medium of exchange. |
VALUE OF MONEY | |
| Time value is the basis for charging interest on capital. | Islamic finance does not recognize the time value of money. Profit on the exchange of goods & services is the basis for earning profit. |
REAL ASSETS | |
| The expanded money in the money market without backing the real assets results in deficit financing. | In Islamic banking, the financial equilibrium or a balanced budget results from the non-expansion of money. |
LOSS SHARING | |
| Interest is charged even in the case, the organization suffers losses. Thus no concept of sharing loss. | Loss is shared when the organization suffers a loss. |
AGREEMENTS | |
| While disbursing cash finance, running finance, or working capital finance, no agreement for the exchange of goods & services is made. | The execution of agreements for the exchange of goods & services is a must while disbursing funds under Salam, Murabaha, & Istisna contracts. |
INFLATION | |
| Due to the nonexistence of goods & services behind the money, while disbursing funds, the expansion of money takes place, which creates inflation. | The presence of goods and services ensures that there is no unnecessary increase in the money supply, thereby preventing the onset of inflation. |
| In response to inflation, the business owner adjusts the pricing of their goods and services. This adjustment is a reflection of the inflationary impact integrated into the product’s cost. | In the Islamic banking system, the entrepreneur does not impose any additional charges as a means of controlling inflation. This principle inherently discourages the accumulation of wealth without purpose |
THE PRESENCE OF CAPITAL GOODS | |
| Bridge financing and long-term loan lending are not made based on the existence of capital goods. | Musharakah & Diminishing Musharakah agreements are made after making sure of the existence of capital goods before disbursing funds for a capital project. |
GOVERNMENT LOANS | |
| The government very easily obtains loans from the Central Bank through Money Market Operations without initiating capital development expenditure. | The government can not obtain loans from the Monetary Agency without making sure of the delivery of goods to the National Investment Fund. |
GROWTH OF WEALTH | |
| The real growth of wealth does not take place, as the money remains in few hands. | Real growth in the wealth of the people of the society takes place, due to the multiplier effect and real wealth goes into the ownership of a lot of hands. |
PROJECT LOANS | |
| Due to the failure of the projects the loan is written off as it becomes a nonperforming loan. | Due to the failure of the project, the management of the organization can be taken over to hand over to better management. |
DEBT FINANCING | |
| Debt financing gets the advantage of leverage for an enterprise, due to interest expense as a deductible item from taxable profits. This causes a huge burden of taxes on salaried persons. Thus the saving and disposable income of the people is affected badly. These results decrease the real gross domestic product. | Sharing profits in the case of Mudarabah and sharing in the organization of business ventures in the case of Musharakah, provides extra tax to the Federal Government. This leads to minimizing the tax burden on salaried persons. Due to this savings & disposable income of the people increased, which increases the real gross domestic product. |
IMPACT ON GDP | |
| Due to a decrease in the real GDP, the net export amount becomes negative. This invites further foreign debts and the local currency becomes weaker. | As the real GDP experiences an upswing, the sum of exports surpasses that of imports, reflecting a positive net export figure. This favorable scenario bolsters the strength of the domestic currency. |
Role of Specialized Knowledge in Islamic Banking VS Conventional Banking
A notable difference between Islamic banking and conventional banking is evident in the educational and certification paths offered to aspiring professionals and those seeking knowledge in the field. To excel in Islamic banking, one needs to possess specialized knowledge and skills, often acquired through the best Islamic banking education programs. This includes online Islamic finance certification, comprehensive Islamic banking courses, and even online diploma in Islamic banking and finance. These educational platforms offer rigorous training and insights into the principles, methodologies, and legal aspects of Islamic finance, which sets it apart from conventional banking. Studying from such dedicated programs helps professionals understand and navigate the complexities of this unique financial system.
Islamic Finance VS Conventional Finance: A Comparative Analysis
In conclusion, the difference between Islamic banking and conventional banking is significant. While conventional banking follows a traditional interest-based system, Islamic banking and finance operate on principles of fairness, sharing risk, and social responsibility. This not only benefits society but also promotes a more stable and sustainable economy. With its emphasis on ethical financial practices, Islamic banking offers an alternative option for customers who want their money to be used ethically. Islamic banking VS conventional banking represents a growing trend globally, as Islamic banking gains momentum through its commitment to fairness, social impact, and adherence to ethical finance practices.
