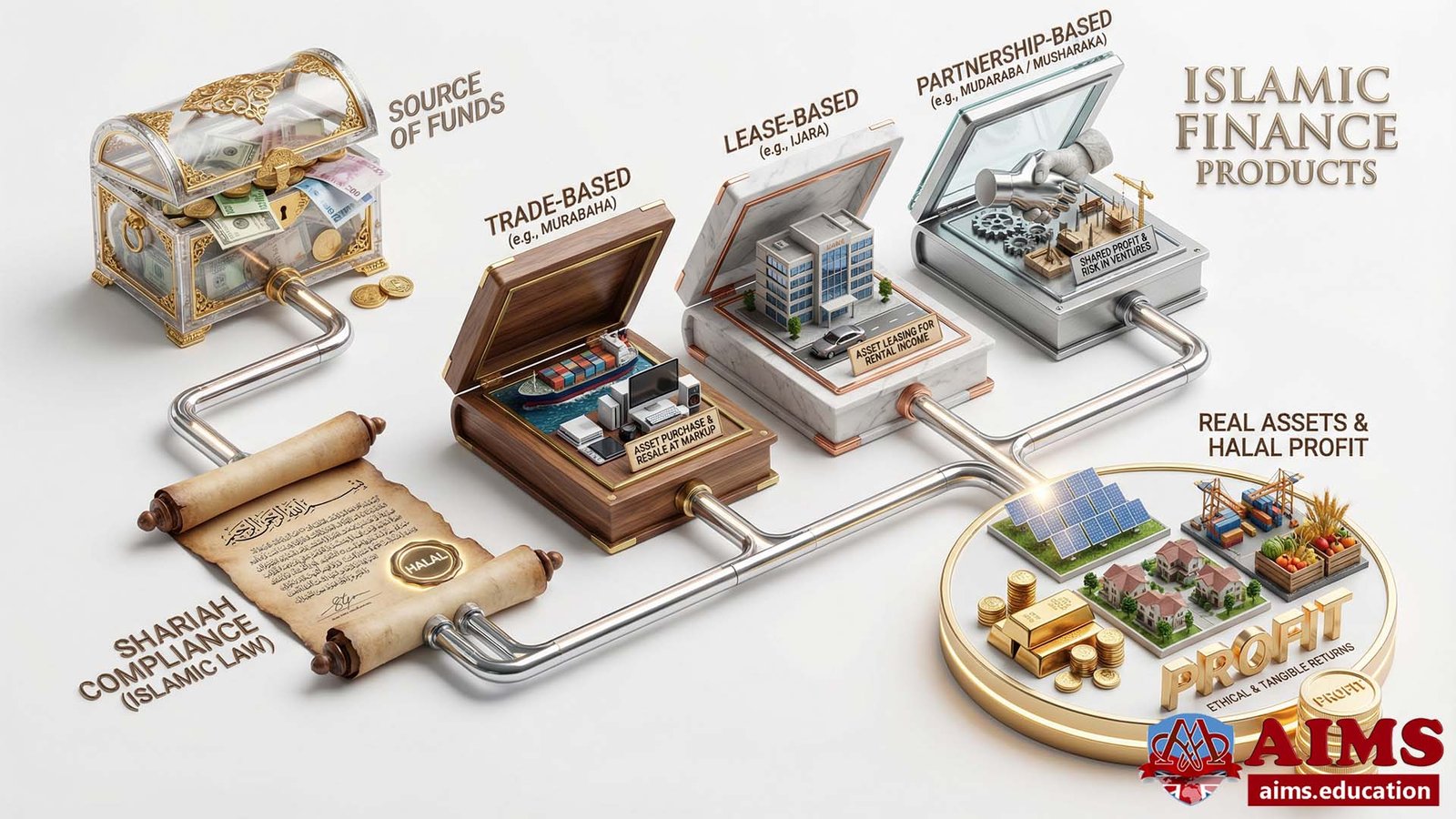
Islamic Finance Products
Islamic financial instruments or Islamic banking products are Shariah-compliant business contracts designed to lend money into assets to earn halal profits. Islamic banking institutions first take ownership of the assets sold or rented. The ownership of the assets is important because, according to a well-known principle of Islamic jurisprudence, “One cannot earn profit from his capital or asset, unless he has have taken risk, or liability of ownership of that capital or asset.” Contrary to that, conventional banks earn interest by lending money. Three main categories of modes of Islamic banking or Islamic finance products exist.
Types of Islamic Finance Products
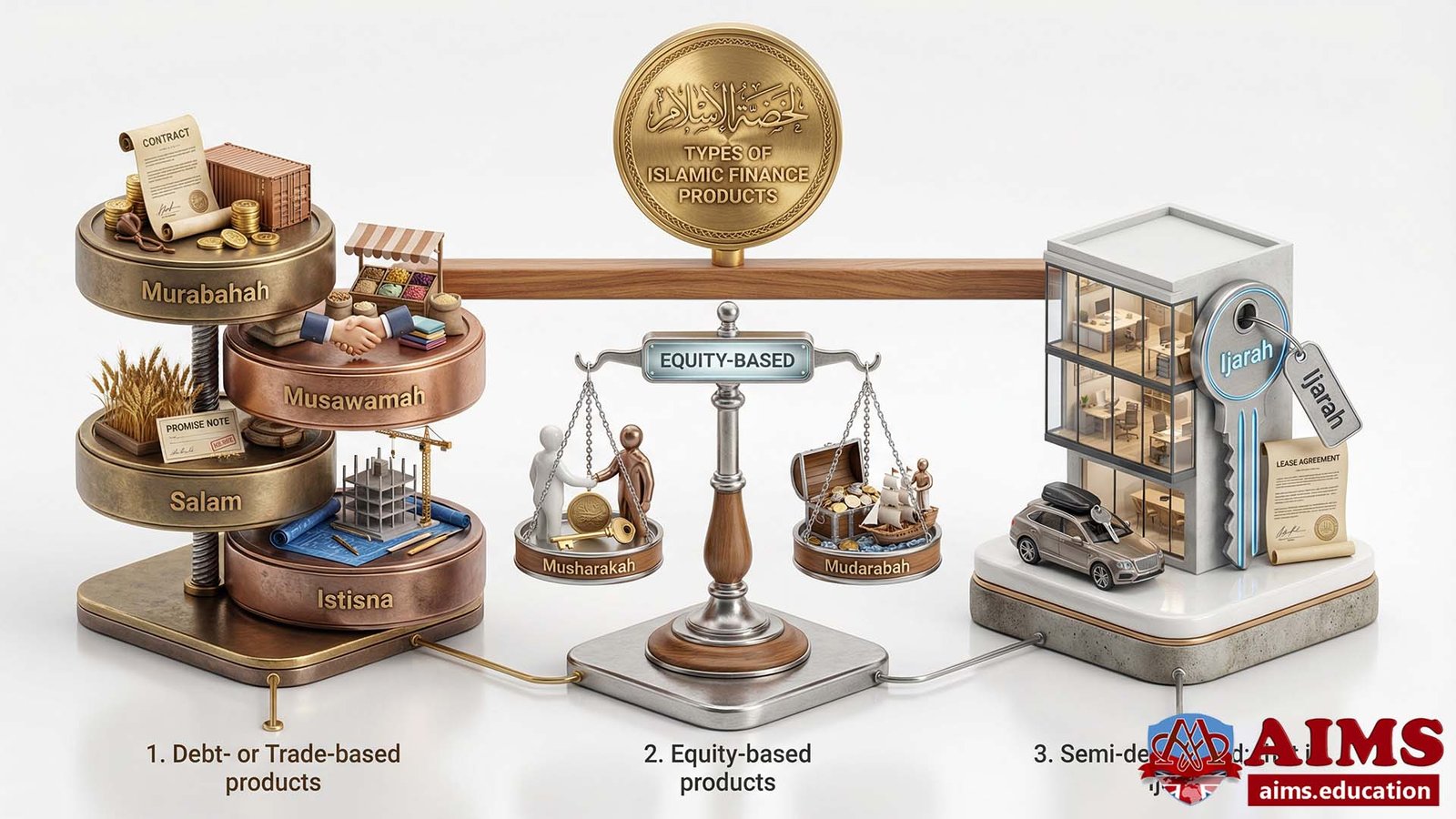
The three categories of Islamic financial instruments are:
- Debt- or Trade-based products, such as Murabahah, Musawamah, Salam, and Istisna.
- Equity-based products, such as Musharakah and Mudarabah.
- Semi-debt based; that is Ijarah.
Equity-based products share the profit based on actual earnings. Because of this, they are more risky than the other two categories, so they are most preferred in Islamic Shariah.
Islamic Banking Products VS Conventional Products
In the case of conventional banking:
- For Asset side products, the bank is the lender, and the client is the borrower.
- For Liability side products, the bank is the borrower, and the client is the lender.
However, the case is different in Islamic banking and financial system. Both types of Islamic finance products are listed below:
| Liability Side Products | Asset Side Products |
| Murabahah | Mudarabah |
| Musawamah | Musharakah |
| Salam | |
| Istisna | |
| Mudarabah | |
| Ijarah |

Overview of Important Islamic Banking Products
Below is an overview of some major modes of financing in Islamic banking:
1. Mudarabah Contract
Mudarabah contract is an Islamic financial instrument in which one party participates with money and the other with efforts. The profit shall be divided in strict proportion, and no party shall be entitled to a predetermined amount of return. Financial losses shall be borne solely by the investor.
2. Murabahah Contract
Murabahah refers to the sale of goods; the profit margin is included in the sale price. The subject of sale must exist, be owned by the seller, and be in his physical or constructive possession. So, the seller assumes the risks of ownership. Murabahah requires an offer and acceptance, which must include Certainty of Price, Place of Delivery, and Date when Price will be paid.
3. Ijarah Contract
Ijarah generally means lease or rent, and it is one of the widely used Islamic banking products. Ijarah is selling the benefit of use or service for a fixed price or wage. The bank makes an asset or equipment available, such as a plant, office automation, or motor vehicle, for a fixed period and rent. The corpus of the leased commodity remains in the lessor’s ownership, and only its usufruct is transferred to the lessee.
4. Musharakah Contract
Musharakah is a business contract established by partners who agree to share business profits and losses. Profits are distributed in the proportion mutually agreed upon in the contract. In this type of Islamic banking product, one or more partners choose to become non-working partners, their profit ratio cannot exceed their ratio in capital investment.
5. Salam Contract
Salam contract is an Islamic mode of financing where the seller undertakes to supply specific goods at a future date, considering a price fully paid in advance at the time of the contract. If the full amount is not paid, it will be tantamount to a sale of debt against debt, Haram.
6. Istisna Contract
It is one of the Islamic banking products where a buyer orders to manufacture, assemble, or construct something at an agreed price and to be delivered at a future date. The commodity must be known and specified, including its kind, type, quality, and quantity. The price must also be fixed in absolute and unambiguous terms and can be paid in a lump sum or instalments, as mutually agreed.
7. Diminishing Musharakah
Diminishing Musharakah is a type of Shirkah where one partner gradually purchases the other partner’s share. According to this concept: “A financier and his client participate in the joint ownership of a property, or equipment, or in a joint commercial enterprise. The financier’s share is further divided into units, and it is understood that the client will purchase those units periodically until all the financier’s units are purchased by the client.

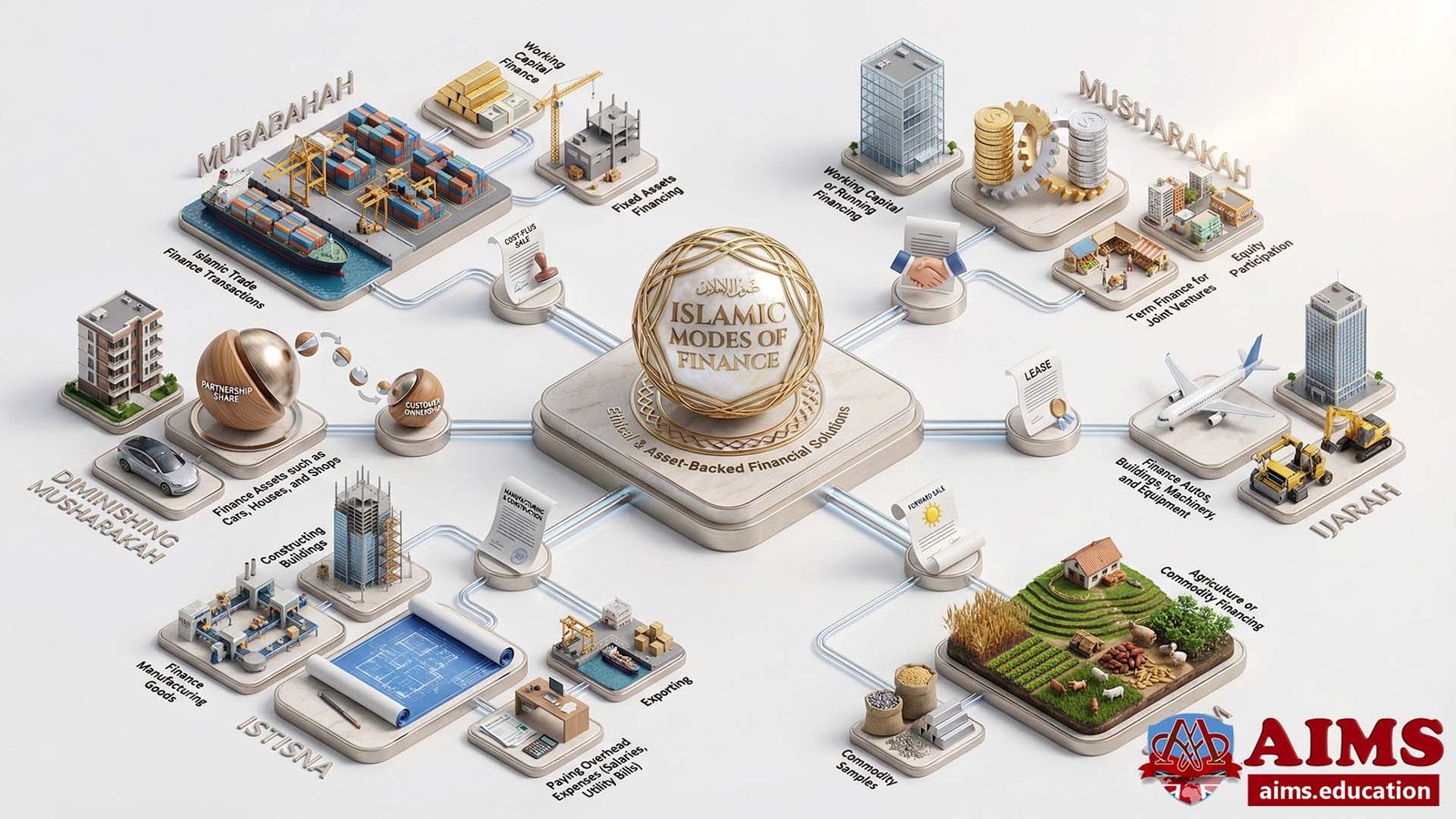
Applications of Islamic Finance Products
- Murabahah is used for Islamic Trade Finance Transactions, Working Capital Finance, and Fixed Assets Financing.
- Musharakah is used for Working Capital or Running Financing, Term Finance for Joint ventures, and Equity Participation.
- Diminishing Musharakah is used to finance assets such as cars, houses, and shops.
- Ijarah, or Islamic leasing, is used to finance Autos, Buildings, Machinery, and Equipment.
- Istisna is used to finance manufacturing goods, constructing buildings, Exporting, and Paying overhead expenses like salaries and utility bills.
- Salam contrat is used for Agriculture or Commodity financing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are Islamic financial instruments and how do they differ from interest-based products?
Islamic financial instruments are Sharia-compliant contracts that link finance to real assets and shared risk. Profit comes from trade, leasing, or partnership—never interest. Banks assume ownership or liability before earning returns, which distinguishes islamic banking products from conventional loans.
Q2: What are the main categories of Islamic finance products?
Three categories exist: trade- or debt-based (Murabahah, Musawamah, Salam, Istisna), equity-based (Musharakah, Mudarabah), and semi-debt-based (Ijarah). Each serves different needs within sharia-compliant financial services.
Q3: How does Murabahah work as an Islamic mode of financing?
The bank buys the asset, bears ownership risk, and sells it to the client at cost plus an agreed profit. Price, delivery place, and payment date must be certain. Murabahah is widely used for trade finance among islamic financial products.
Q4: What is Mudarabah and when is it used?
Mudarabah is a partnership of capital (investor) and effort (manager). Profits are shared by a pre-agreed ratio; financial loss rests with the investor absent negligence. It supports entrepreneurship within types of islamic banking.
Q5: How is Musharakah different from Mudarabah?
In Musharakah, partners contribute capital and may work; profits follow an agreed ratio and losses follow capital share. In Mudarabah, only the investor provides capital and the manager provides effort. Both are islamic modes of financing built on risk sharing.

Q6: What is Ijarah in Islamic banking products?
Ijarah is leasing: ownership stays with the lessor while use transfers to the lessee for rent and time. It finances vehicles, buildings, and equipment, sitting between equity and debt among islamic finance products.
Q7: When are Salam and Istisna appropriate?
Use Salam when goods will be delivered later but the price is fully prepaid—common in agriculture or commodities. Use Istisna for manufacturing or construction with agreed specifications and future delivery. Both are trade-based islamic financial instruments.
Q8: How does Diminishing Musharakah work?
The financier and client co-own an asset. The client gradually buys the financier’s units while paying rent or sharing profit on the remaining share. It’s popular for homes and equipment within modes of islamic banking.
Q9: What real-world applications do islamic banking products cover?
Murabahah: trade finance and working capital; Musharakah: joint ventures and equity participation; Ijarah: autos, buildings, machinery; Istisna: manufacturing and construction; Salam: agricultural or commodity pre-finance. These types of islamic finance tie funding to real assets.
Q10: Why are ownership and risk essential in sharia banking products?
Profit must be tied to ownership risk or liability. Institutions earn returns only after assuming responsibility for an asset or service, which keeps sharia-compliant financial services aligned with real economic activity and avoids interest-based gains.
