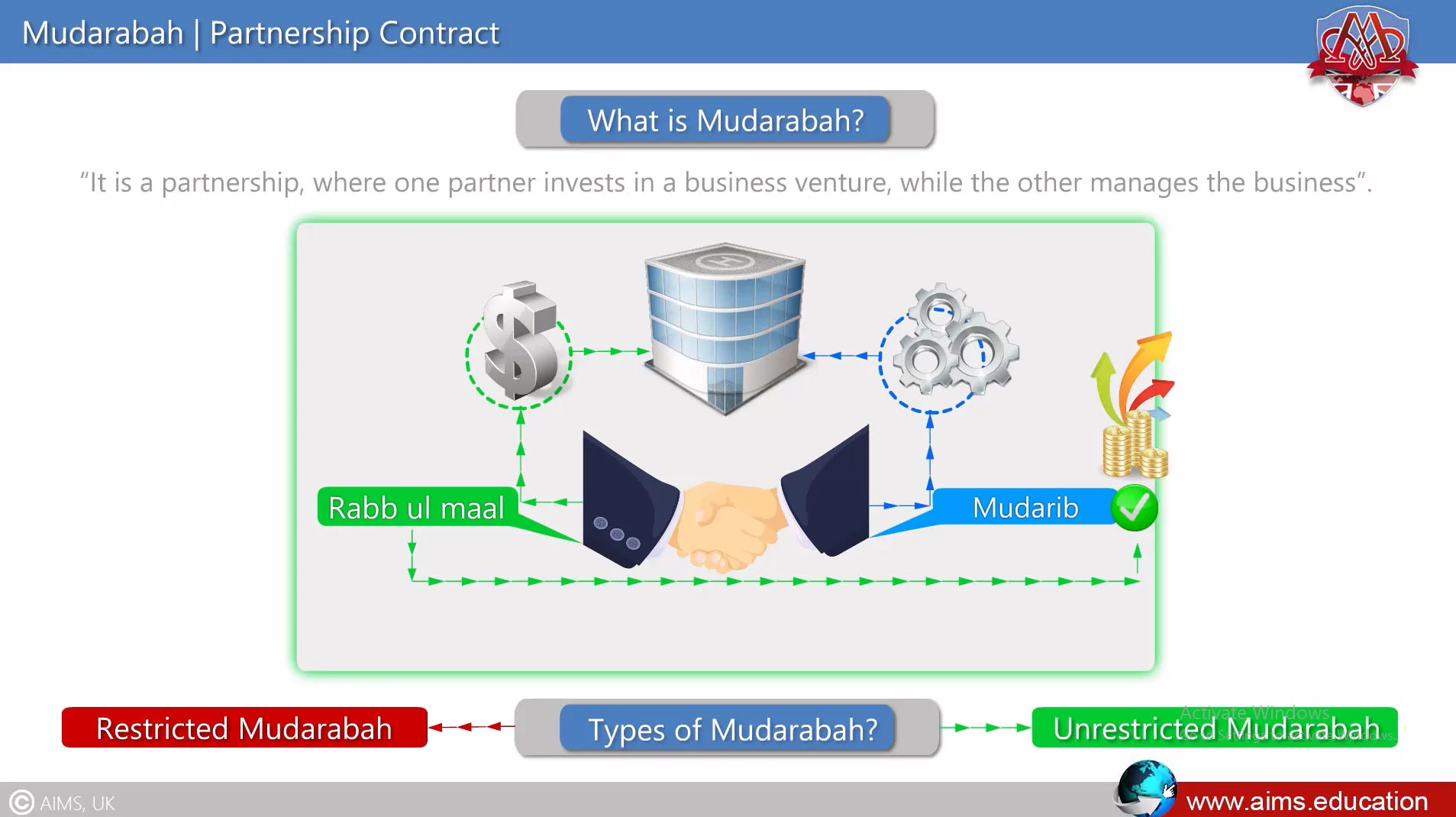
Mudarabah Meaning and Definition:
The Mudarabah contract is a business partnership contract. Let us first understand the Mudarabah definition: “A partnership, where one partner invests in a business venture, while the other manages the business.” In Mudaraba, the person investing is called Rabb-ul-maal, the person who manages the business is called Mudarib, and the investment is called “Raas-ul-Maal.” Mudarabah in Islamic banking is widely used to structure bank deposit accounts, and it is also used in combination with other Islamic financial contracts.
“Two partners plan to open a car showroom. The investing partner or Rabb-ul-maal will be responsible for investing in buying the cars, paying the rent, and making other office expenses. Meanwhile, Mudarib, as a working partner, is responsible for providing skill, expertise, and business management.”.
Mudarabha Example!
Types of Mudarabah
It is divided into two types: Restricted and Unrestricted.
Restricted Mudarabah
It is a contract in which an investor restricts a working partner’s actions to a particular location or type of business.
Unrestricted Mudarabah
In a mudarabah contract, the investor permits the working partner to administer the fund without any restrictions.
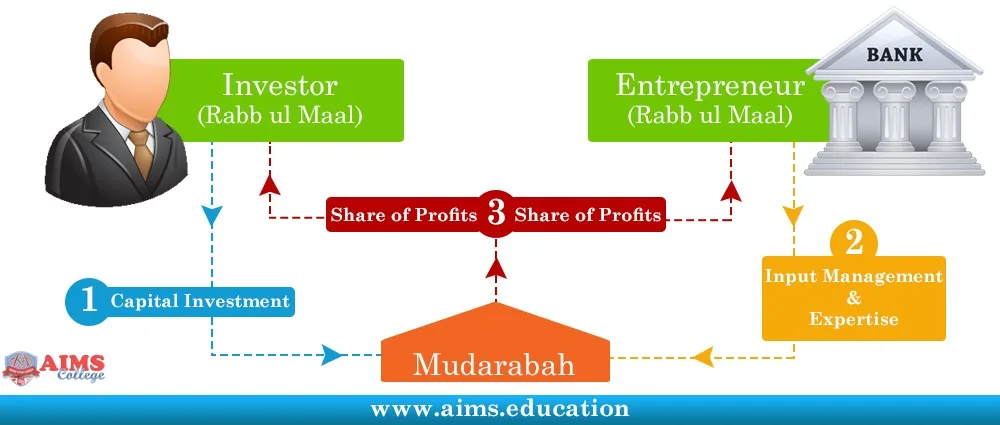
Understanding the Mudarabah Contract
- Investor and Working Partner decide to enter a business venture.
- The investor provides capital to run the business, and the Working Partner is responsible for running and managing the business through his expertise.
- Subsequently, if the venture is successful and generates profit, this profit is distributed among both partners on a pre-determined ratio.
Mudarabah Examples
1. Islamic Current Account
In Islamic Banks, current accounts are opened on the basis of an “Islamic or Halal Loan” to the bank, so the principal is guaranteed, and no facility can be given to the account holders.
2. Islamic Saving Accounts
- They are term deposits in a combination of Shirkah and Mudarabah.
- Constructive liquidation is done every month or half-yearly.
- Physical liquidation is usually not possible in the banking system.
- While calculating the profit ratio, “Administrative Expenses” are deducted from depositors, and branch or operational expenses are deducted from total portfolio.
3. Islamic Project Financing
If the Financier wants to finance the whole project, it is Mudarabah. However, if the investment comes from both sides, it is Musharkah.
4. Islamic Working Capital Financing
Working capital finance could be provided only through Musharkah financing. The amount invested by the Financier will be treated as its share of the investment. Financier’s share in profit should not exceed the percentage of its investment.
Mudaraba with Other Islamic Modes
- Under the Mudarabah principle, the customer is an Investor, and the bank is the manager of the funds deposited by the customer.
- The bank allocates those funds to a deposit or investment pool.
- Pool funds are used to finance customers under Islamic modes, such as Murabahah, Ijarah, Istisna, Musharakah, Diminishing Musharakah, etc.
- Profits earned through these modes are distributed among the bank and depositors.
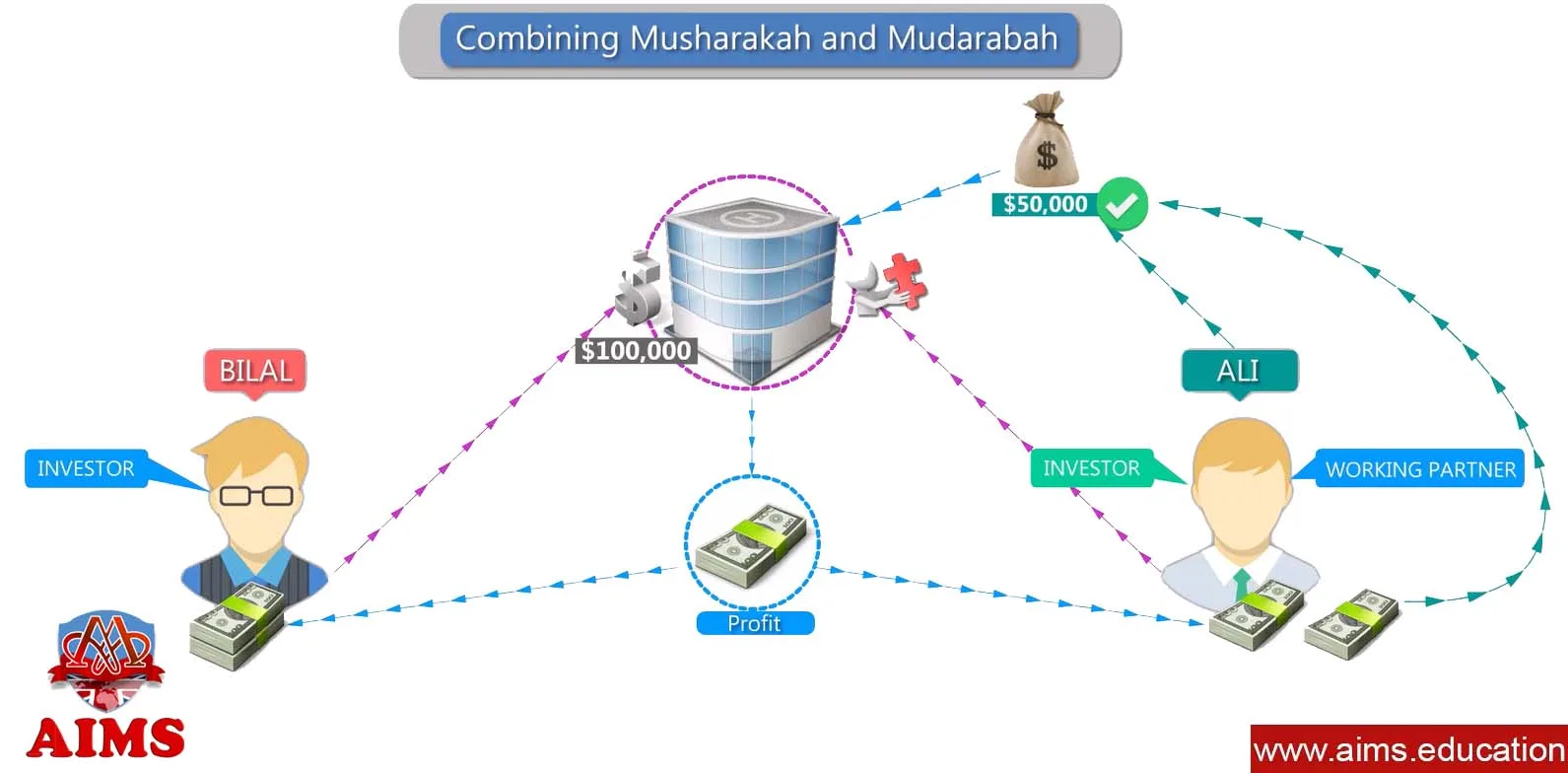
Combining Musharakah and Mudaraba Contracts
Working partners may also invest money in the business; in this case, Musharkah and Mudaraba are combined.
Case Study
“Ali” and “Bilal” start a Mudarabah business, and it is agreed that “Bilal” will invest $100,000, and “Ali” will share the profit as a working partner on an agreed ratio. Suppose that after some time, more investment is needed, and “Ali” adds $50,000 with the permission of “Bilal.” So, in that case, “Ali” will take profit:
- As an “Investor” against his investment of $50,000, and;
- As a “Working Partner” for managing the whole business worth $150,000.
Two-Tier Mudarabah in Islamic Banking
Almost all Islamic Banks are using this Mudaraba-based liability structure, where:
- The Islamic bank first signs an agreement with the depositors as a Managing Partner of their funds and;
- Then, the Islamic bank signs an agreement with the Entrepreneur as an Investor.
- This model is a hybrid of Musharakah and Mudaraba.
- Islamic banks also commingle Islamic Banking Fund, especially when there is a single pool for PLS-based deposit products.
The Islamic finance certificate, part of our diploma in Islamic banking and finance, discusses this topic in more detail, including its mechanism, applications, Islamic accounting, and AAOIFI Auditing Standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is mudarabah in Islamic banking?
Mudarabah is a profit-sharing partnership: the investor (Rabb-ul-maal) provides capital and the Mudarib manages the venture. Profits are split by ratio; normal business loss is borne by the investor.
Q2: What is the mudarabah meaning and definition?
Mudarabah means a partnership of capital and management. One party funds; the other runs the business. Profits are shared by ratio; no guaranteed return.
Q3: What does mudharabah meaning refer to? Is it the same as mudaraba/mudarabah?
Yes. Mudharabah, mudaraba, and mudarabah are alternative spellings of the same Shariah contract.
Q4: What is a mudarabah contract?
A formal agreement setting the profit-sharing ratio, scope, reporting, expense treatment, and negligence standards. It does not guarantee principal or a fixed return.
Q5: What are the types of mudarabah?
Restricted mudarabah (limited mandate) and unrestricted mudarabah (broad discretion) within Shariah-compliant investments.
Q6: How are profits and losses shared in a mudaraba?
Profits: by agreed ratio. Losses: borne by the investor unless caused by misconduct or negligence; the Mudarib loses effort/time.
Q7: How do Islamic banks apply mudarabah in deposit accounts?
Through two-tier structures: depositors → bank (Mudarib), then bank → entrepreneurs (investor). Profits from Shariah assets are pooled and shared.
Q8: Can a mudarabah be combined with Musharakah?
Yes. If the working partner adds capital, they share as a Musharakah partner on that capital while remaining Mudarib on investor funds.
Q9: Is “mudarba” a correct term?
It’s a common shorthand for mudaraba/mudarabah. Use “mudarabah” for formal writing.
Q10: What clauses should a mudarabah agreement include?
Profit ratio, scope (restricted/unrestricted), expense policy, accounting/reporting, rules for pooling funds, negligence standards, and dispute resolution.
