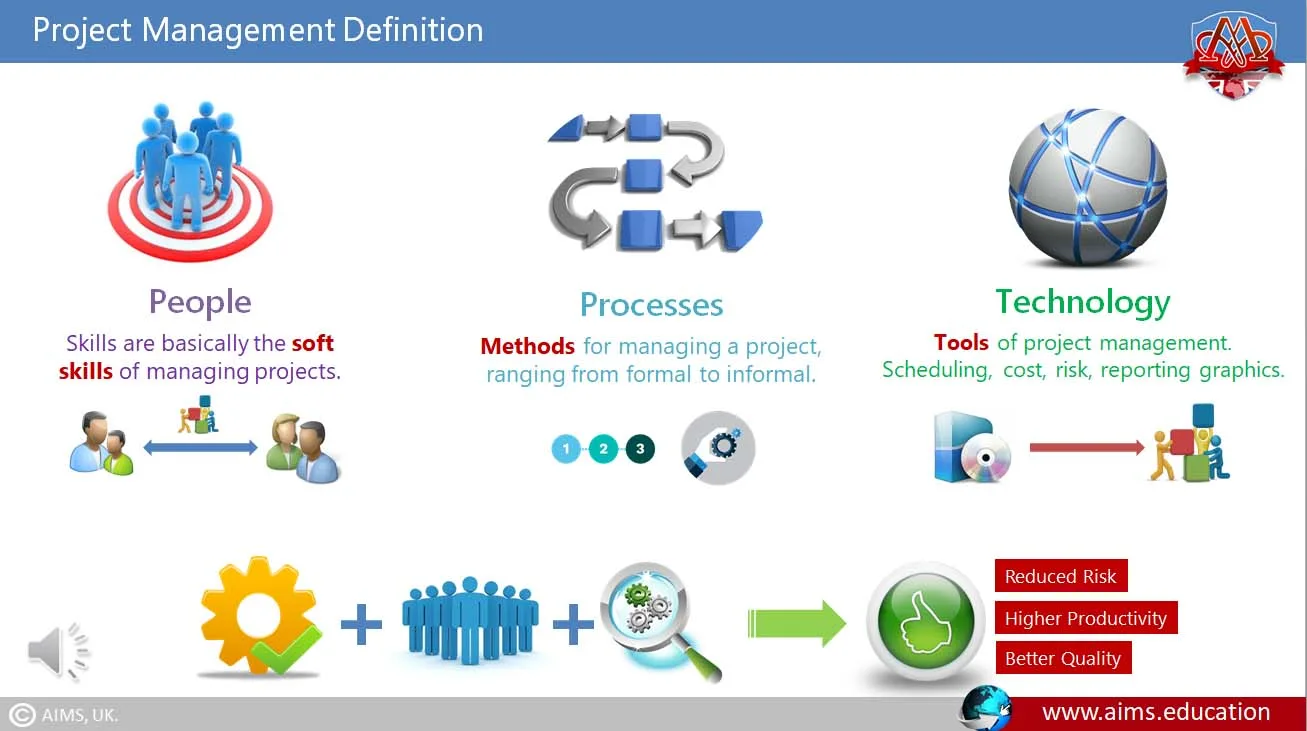
What is Project Management?
According to the project management definition, it is a structured process for planning, organizing, and tracking a project from its beginning to its conclusion. Project management is one of the prime competencies in the business world today that aids organizations as well as individuals in getting results. Resources, people, money, materials, and time are to be streamlined to meet an objective under given constraints with respect to cost and time. Basically, it is the art and science of minimizing the uncertain risks involved in a project by using resources efficiently to achieve desired results simultaneously.
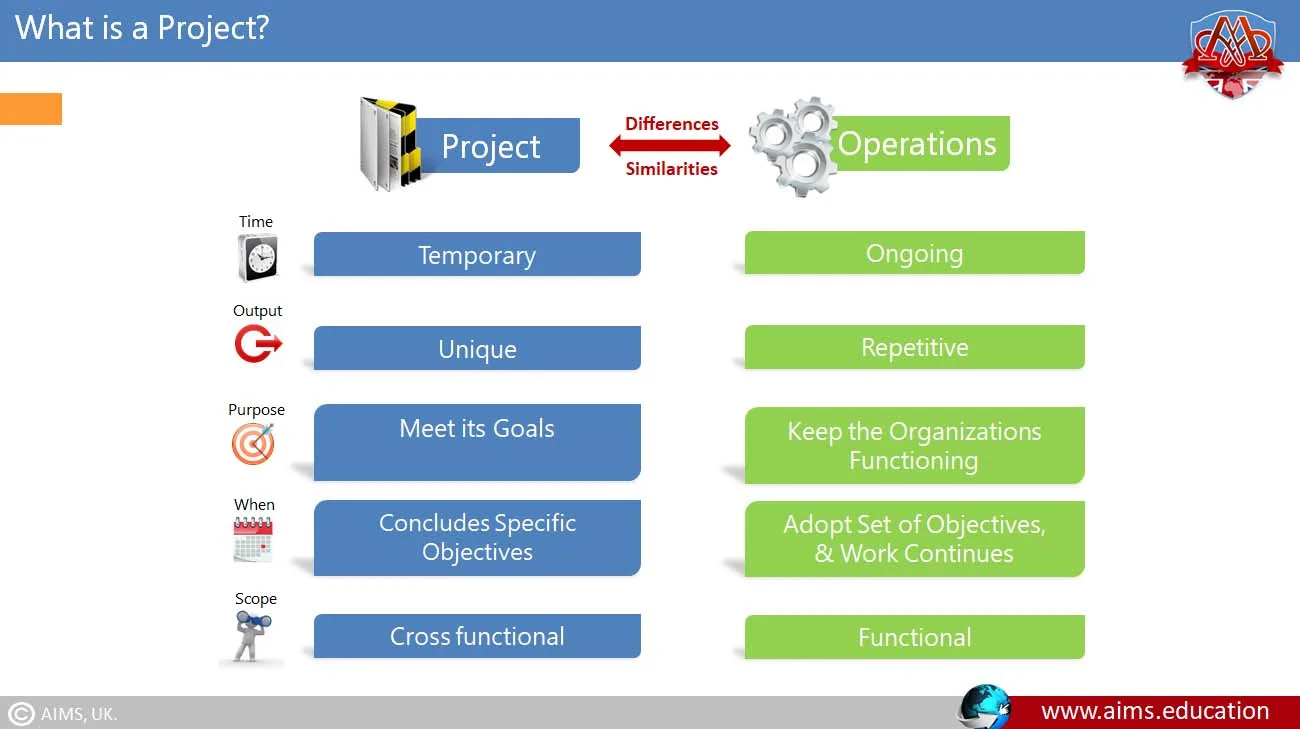
What is a Project?
A project is a temporary endeavour to accomplish something unique, something that can be a product, a service, or a result. It has a definite objective; hence, it has both a particular starting point and a finishing point, and it does have a definite scope of work with assigned resources. Each project performs almost as a small organization in its own right, very close to the firm’s more comprehensive strategic objectives.
Key are the key points to remember :
- Temporary: Projects are temporary and have specific ends.
- Unique: Each project produces a different product, service, or result.
What are Project Objectives and Purpose?
Project objectives are concrete, measurable targets that would be achieved if a project were implemented successfully. Objectives provide the basis for all planning and implementation.
1. Solution of a Specific Problem:
The prime motive of any project is the solution to a particular problem or need that an organization, or for that matter, a market, is facing to find an effective and workable solution.
2. Deliver Value:
Typical centre-based objectives involve creating measurable value for stakeholders by developing a new product, improving processes, or innovating services.
3. Stakeholder Requirements:
One of the major goals is satisfying the stakeholders’ requirements, balancing the varied interests of many different stakeholders against the capabilities and constraints of a project.
4. On Time:
Completing any project within the envisaged time ensures that all intended benefits are realized.
Project Examples
Projects range from single-day projects to multiyear projects in scope, complexity, and impact. Projects would vastly differ, for while some are simple to do, quite small, and of little consequence—performed in less than a day—some are gigantic because of the complexity involved and done for years to finish. Some examples of projects are as follows:
1. Home Renovation
A personal project to redesign or give one’s home a facelift.
2. Website Launching
A technical project manager creates and launches a website for one’s online presence.
3. Community Garden
This local initiative aims to promote sustainable living and community contact.
4. Marketing Campaign
A strategic project aiming at gaining market share by promoting products or services.
5. Software Development
A project to develop a new application or system to satisfy certain user needs.
6. Organizational Restructuring
A corporate project aiming at making the firm’s operation more efficient and effective.
7. Urban Development Plan
Large civic projects are implemented by planning a city with the required infrastructure and public facilities.
8. Research and Development
A development-oriented program with a technological, chemical, pharmaceutical, or innovative slant.
9. National Health Initiative
Government-sponsored projects aimed to improve the health standards of every citizen across the country.
10. International Space Station Expedition
International science program on the betterment of human understanding in space.
Real-World Project Management Examples
Let us examine some real-world examples to better understand project management in practice.
Example 1: NASA’s Appolo
One notable example is NASA’s Apollo program, which successfully landed humans on the moon for the first time in 1969. This ambitious and complex program comprised several projects and utilized various project stages and activities in a planned manner.
Example 2: Hoover Dam in the United States
Another well-known example is the construction of the Hoover Dam in the United States, which follows a step-by-step progression from planning and design to construction and completion.
7 Key Components of Project Management
It is the process of guiding a project from its initiation to the delivery of desired outputs, within predefined performance parameters. The basic components of project management are:
1. Leadership and Team Management
Effective leadership and cohesive team management become the prime factor of success for the project. Role of project manager is to motivate, guide, and control team dynamics toward a common goal.
2. Time Management and Meeting Deadlines
Correct estimation and scheduling of all tasks, coupled with regular monitoring, ensures time management within project management and meeting deadlines, which aids in maintaining the project’s integrity and credibility.
3. Adaptability and Problem Solving
Turn uncertainties into preparation for the ability to handle any uncertain situation in PM by innovatively solving problems.
4. Resource Allocation
Resources, when properly and efficiently applied, will increase human, financial, and physical resource use, hence, adequate supply to all parts of the project.
5. Strategic Planning and Execution
It is indeed at the heart and soul of any project management course—that is, planning much closer to perfection and executing to reach all the goals that were placed.
6. Risk Assessment and Mitigation
This involved identifying all potential risks that might disrupt the program and laying down mitigation plans to minimize this disruption and ensure success.
7. Continuous Communication
Regular and proper communication with stakeholders is one of the successful project management objectives, and it develops an atmosphere of openness and faith.
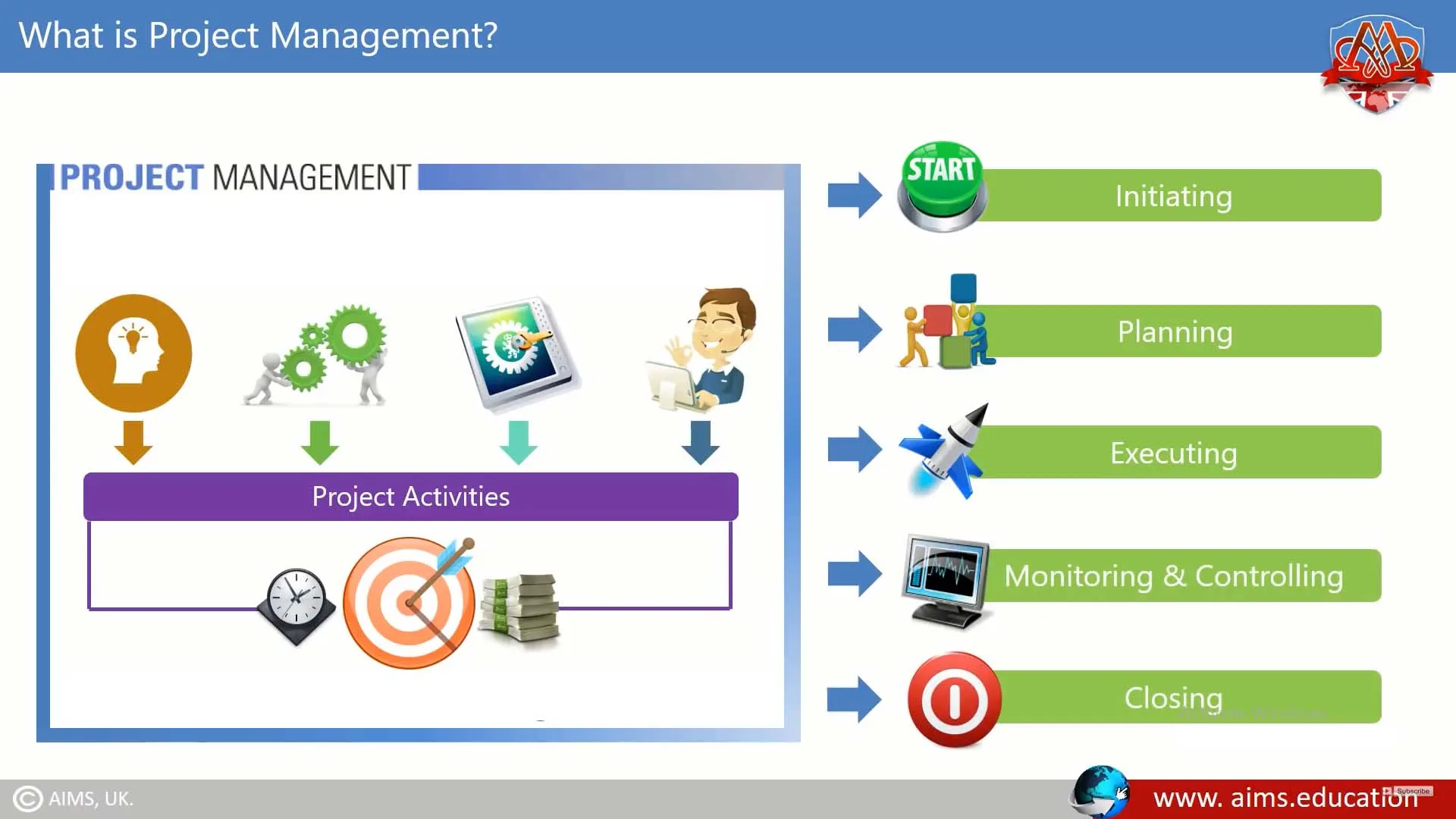
Project Management Phases
PM is divided into key phases, which map from concept to completion. They are summarized below; for a detailed review, see the key project management phases.
1. Initiation
It is the start of a project where the objectives are defined. It deals with the most fundamental question of how to start a project and its purpose and ensures alignment with business goals.
2. Planning
This is the backbone of project management, involving scope, time, resources, and procedures for the execution of a project.
3. Implementation
This is the stage at which a plan is brought into action through activities from the project team that aim to realize the project’s objectives.
4. Monitoring and Controlling
This is the stage where the progress will be tracked, often running parallel to Execution to keep the project on course.
5. Closure
This is the final stage in PM, where the project is formally closed and delivered to the client or stakeholder.

Popular Project Management Methodologies
PM comes in many forms, each fitting different projects and teams. Four popular types are given below, and see the 7 project management methodologies to understand them in more detail:
1. Waterfall
Sequential Systematic Approach The Waterfall method is a linear project management model in which every phase has to be completed before the next one is started. This can be recognized by its sequential systematicness, which allows for making schedules and easy following up on the work.
2. Agile
Agile project management thrives on adaptability. It implies breaking down work into small increments and delivering them with customer collaboration. Software development teams widely use it.
3. Kanban
Work Management Visualized using a Kanban board that shows all stages of work through tasks and respective columns for each stage along a workflow.
4. Scrum
Scrum project management is an iterative framework that uses Agile methodology. Teams work in short sprints, ranging from two to four weeks. This enables them to break it down into manageable bits and adjust priorities according to need.
However in some cases, a hybrid model is also used, which combines the benefits of multiple methodologies. Agile-Waterfall Hybrid Method is a popular example of hybrid project management.
Importance of Project Management in Organizational Success
It is key to the success of any business and the efficient working of organizations. It translates visionary ideas into real accomplishments by employing a strategy known as execution, performed diligently with oversight.
1. Strategic Plan
Thus, PM forms the platform for setting specific yet realistic objectives and monitoring all phases consistent with resources, effort, and activity.
2. Art and Science of PM Merges
The art of good PM aligns different functional units in a coherent, well-structured way that transforms chaos into progress.
3. As Corporate Compass
PM has been the orientation in a fast-changing world, keeping projects focused toward the strategic business goals and mitigating associated risks, steering projects to success.
Evolution of Project Management in the Global Arena
The industry is increasingly shaped by globalization and technological advancements. The rising demand for online project management courses democratizes access to knowledge. AIMS programs allow professionals to acquire qualifications from the comfort of their homes. Advanced programs like an online MBA in project management are developing the next generation of leaders with theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Efficiency, adaptability, and innovative problem-solving will keep PM at the forefront of business practice for years.
<section aria-labelledby=”faq-title”>
<h3 id=”faq-title”><span style=”color: #ff9900;”>Frequently Asked Questions</span></h3>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q1: What is project management?</h4>
<p>Project management is a structured process to plan, organize, and control work from initiation to closure so objectives are achieved within time, scope, and cost constraints.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q2: How is a project defined in project management?</h4>
<p>A project is a temporary endeavor that delivers a unique product, service, or result with a defined start, finish, scope, resources, and success criteria.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q3: What are the key objectives of project management?</h4>
<p>Typical objectives are solving a specific problem, delivering measurable value, satisfying stakeholder requirements, and finishing on time while meeting scope, quality, and budget.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q4: Which components are essential in project management?</h4>
<p>Leadership, time management, adaptability, resource allocation, strategic planning and execution, risk mitigation, and continuous communication.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q5: What are the five phases of the project lifecycle?</h4>
<p>Initiation, planning, implementation, monitoring and controlling, and closure.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q6: When should Agile vs. Waterfall be used?</h4>
<p>Use Waterfall for stable, sequential work; Agile for evolving requirements and iterative delivery. Hybrids can balance both.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q7: What are examples of real-world projects?</h4>
<p>From home renovation and website launches to national health initiatives and space exploration, including NASA’s Apollo and the Hoover Dam.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q8: Why is stakeholder communication critical?</h4>
<p>It aligns expectations, surfaces risks early, and builds trust so teams can balance diverse needs with project constraints.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q9: How does risk assessment support project success?</h4>
<p>By identifying threats to scope, schedule, or quality and applying mitigation plans to reduce likelihood or impact.</p>
</div>
<div class=”faq-item”>
<h4>Q10: How do time management and deadlines affect outcomes?</h4>
<p>Accurate estimates, realistic schedules, and routine monitoring keep delivery on time and preserve benefits realization.</p>
</div>
</section>
