Gharar Meaning in Islam:
Gharar (الغرر) means uncertainty, hazard, chance or risk. Islamic dictionary describes it as “The sale of what is not present”. Now let us understand, what is gharar in Islamic banking. In Islamic banking, it may be defined as: “The uncertainty that is present in the basic elements of an agreement is the wording, subject matter, consideration, and the liabilities”. As a matter of fact, it is one of those impediments, which limit the power of decision making. An agreement, that has any element of gharar (بيع الغرر), which is not valid from the Shariah point of view.
Prohibition of Gharar in Hadith:
Let us understand what is gharar, with the help of some examples, in the light of Ahadith:
- Sale of unborn Camel’s baby, still in the Mother’s womb;
- Flowers, before they appear on the plant;
- Milk in the Lactose Glands;
- Fish that comes in one throw of net;
- Fruits on the Tree from mere estimation;
- Any one of the animals from the herd; and;
- Wool on the body of the animal.
“Gharar is an Arabic term derived from the root verb “Ghar” and it means “risk”. In Islam, it refers to the peril of losing something valuable. If a person uses their money to invest in business and the business goes bankrupt, that is one way they can lose all of thier investment. Gharaar is not necessary monetary loss. It could also reference loss of property or bodily injury.”.
Gharar Meaning!
Comparison of Gharar with Few Shariah-Prohibited Elements
1. Jihalah
Jihalah means unawareness or blindness, and it is one of the causes of الغرر. For example, a transaction can be known from all angles, but Subject Matter’s delivery can be difficult.
2. Qimar
Qimar is an event, in which there is a possibility of total loss to one party. Every gambling is a form of Qimar, but it is not limited to gambling.
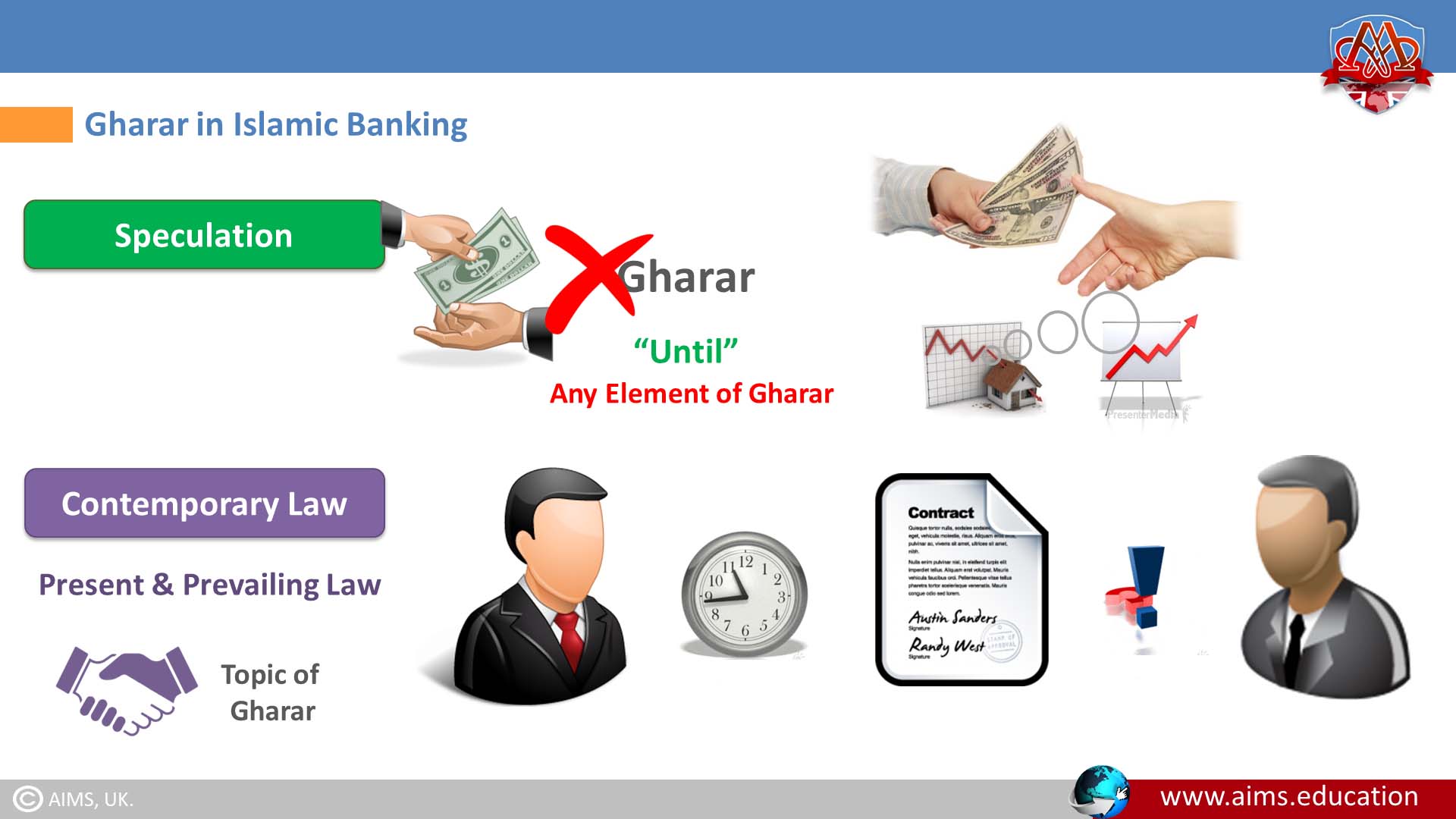
3. Speculation
Every speculative transaction is not gambling/maysir (maisir) until it has any element of it. This is because these activities are carried out in the hope of profiting from the rise and fall of the prices of commodities or assets.
4. Contemporary Law
It means the present and prevailing law, and it also deals with the topic of Gharar in Islamic banking. The Contract in which any party in the agreement, at the time of execution of the agreement, cannot decide as to how much it would give or take.”
Examples of Gharar
First Example: Sale of Unharvested Crops
For example, one of the many instances where gharar is involved would be regarding the sale of crops before they have even been harvested. Here, neither buyer nor seller knows for certain that the crops will live to be harvested or how good they will even be at harvest time (or what quantity would actually survive and/or grow). This is a transaction that contains high risks and potential deception; due to these uncertainties, this type of sale accounts for gharar.
Second Example: Sale of Contested Property
The sale of a property that is under legal dispute, is a form of الغرر. Those who sold and bought were unsure of the eventual result with respect to property ownership. In this scenario, the buyer is unsure of what they are buying and at risk of losing; hence it’s gharar.

Types of Gharar
The three main types of gharar known by Islamic law are as follows:
1. GHARAR AL-FAHISH
This refers to high-risk transactions whose predictability is not possible. In this type of Gharar, both buyers and sellers have no knowledge of the outcomes of the transactions. Speculative investments and gambling are some key examples.
2. GHARAL AL-MUZABANA
This is another kind of ghara, in which working conditions are not clear. In other words, it is a kind of gharar in which the outcome or decision is made by one or both parties due to the uncertainty of the terms and conditions.
3. GHARAR AL-TASWIR
It is an uncertainty caused by a lack of information about the risk. This occurs when one party does not have the proper information regarding the transaction, with the information-receiving party having all the information. It is prohibited in Muslim Law because it results in exploitation.
Educational Opportunities in Islamic Finance
AIMS offers different educational avenues, that can provide individuals with knowledge on Islamic finance. Individuals seeking extensive research and top-tier positions should consider PhD in Islamic Finance. On the other hand, the masters degree in Islamic Banking and Finance provides individuals with most of the knowledge needed for one to understand what Islamic banking entails. AIMS Islamic finance diploma provides candidates with the necessary skills to specialize in Islamic finance without intensive knowledge. AIMS’ online training course allows students and professionals to learn at their convenient time.
Causes of Gharar?
To eradicate Gharar, and thus comply with the laws of Shari’a, institutions dealing in Islamic banking and finance must understand these causes:
- It happens typically when all details are not time fully disclosed about a transaction, leading to information Asymmetric.
- It is supported by incomplete contracts. Such ill-defined contracts may create confusion and dispute among the parties.
- It can be caused by unpredictable things or fortuitous events such as natural disasters (especially in contracts relating to agriculture or real property).
- If one party deceives the other side and cheats them, they use gharar.
How to Avoid Gharar in Trade
When it comes to trade, gharar creates many problems for both sides.
- It reintroduces an element of inequity into transactions by breeding uncertainty or deceit — risk.
- Its presence in trade agreements may give rise to unfair enrichment or loss, leading to disputes and deteriorating the good faith of its parties.
- It makes any business contract that contains this form a null and void in all Islamic financial instruments.
In conclusion, traders need to pay attention and find the symptoms of الغرر, which can ruin their transactions concerning maintaining Islamic banking and finance principles defined by Islam.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is gharar in Islamic banking?
Gharar is excessive uncertainty in a contract’s core elements—subject matter, price, wording, or liabilities—making the deal potentially void under Shariah.
Q2: What does “gharar” mean in Islam?
It literally means uncertainty or risk. In law, it covers transactions where the outcome or deliverability is unknown, risking injustice.
Q3: Why is gharar prohibited by Hadith?
Prophetic narrations forbid sales of unknown or non-existent items (e.g., unborn animals, unharvested crops) due to embedded uncertainty and deception.
Q4: What are practical examples of gharar?
Examples include selling contested property, an unspecified animal from a herd, milk in the udder, or produce before it forms or ripens.
Q5: What are the main types of gharar?
Gharar al-Fahish (excessive risk), Gharar al-Muzabana (unclear terms/conditions), and Gharar al-Taswir (information asymmetry leading to uncertainty).
Q6: How is gharar different from jihalah and qimar?
Jihalah (ignorance) can trigger gharar; qimar is a zero-sum outcome like gambling. Gharar is broader and stems from contractual uncertainty.
Q7: Is all speculation gharar or maysir?
No. Speculation becomes problematic when uncertainty or zero-sum outcomes create prohibited elements, harming fairness between parties.
Q8: What typically causes gharar in contracts?
Ambiguous terms, incomplete contracts, information asymmetry, deceptive behavior, or unpredictable events affecting ownership or delivery.
Q9: How can businesses avoid gharar?
Specify quality, quantity, price, delivery, and ownership; ensure deliverability; remove ambiguous clauses; and disclose all material facts.
Q10: When does gharar invalidate a contract?
When uncertainty impacts core elements (existence, ownership, or deliverability), it becomes excessive and may render the contract void.
Q11: Can you give a simple example of gharar al-fahish?
Selling unharvested crops: outcomes are highly uncertain, so the risk is excessive and the sale is not permitted.
Q12: How do “types of gharar” guide practice?
They help identify where uncertainty is unacceptable and inform contract design with clarity, disclosure, and enforceable terms.
