What is Islamic Capital Market?
At its heart, the Islamic Capital Market is one where transactions for Shariah-compliant financial assets are handled. Unlike conventional capital markets, Islamic capital market instruments and products are compliant with Shariah rules, which encourage and enable investors to invest in halal investment opportunities. Whereas a conventional capital market simply enables investors to make investments and borrowers to find funds to borrow. For those who wish to only invest and carry out transactions in the Islamic capital market products, there are several products they can avail. Islamic capital market instruments enable financial activity from remaining activity without disobeying Shariah. Islamic capital market instruments include Murabahah Sukuk, Ijarah Sukuk, Partnership Sukuk, Ordinary Stocks, Preferred Stocks, Islamic Mutual Funds, and Single Stock Features.
7 Key Islamic Capital Market Instruments and Products
Following are the seven key Islamic Capital Market instruments:
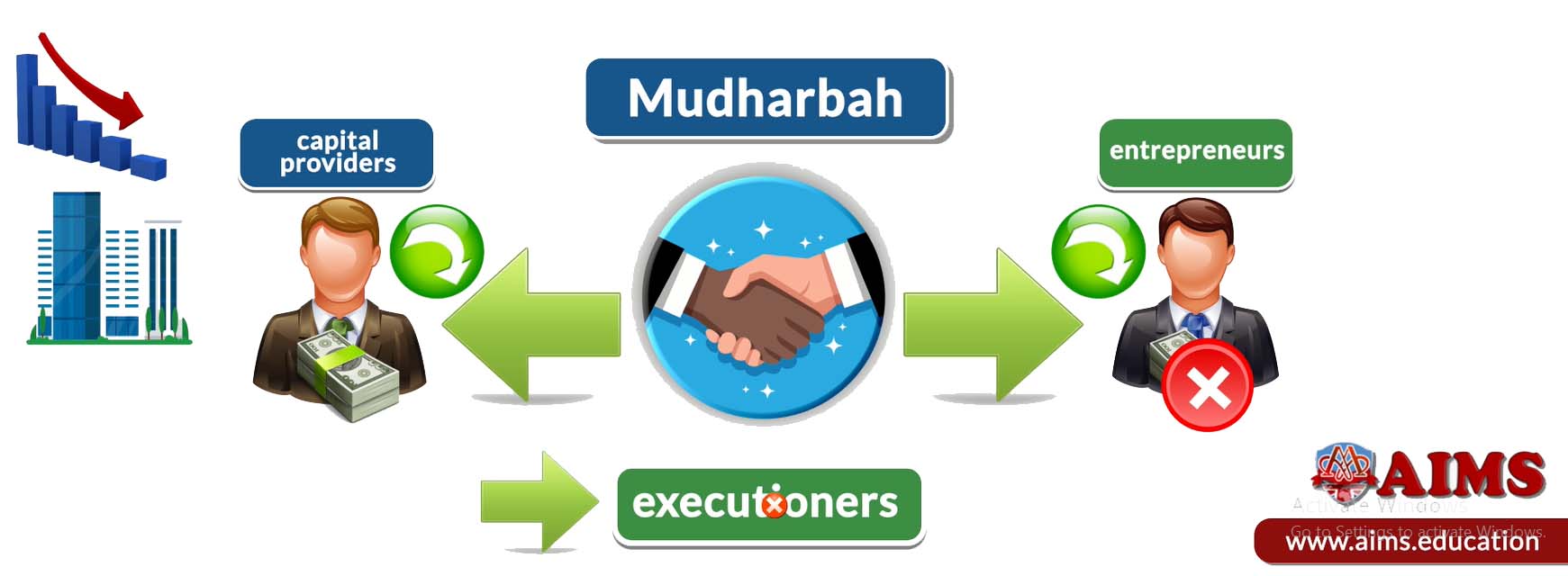
1. Mudarabah Sukuk
Sukuk (Islamic bonds) are certificates representing ownership in investments, and Murabahah Sukuk are managed on the principles of Mudaraba. An essential form of profit-sharing in Islamic finance, Mudaraba sits on a foundation made by agreement between capital providers and entrepreneurs, or essentially, the “executioners”. With the establishment of an enterprise aimed towards generating “halal” profit, both parties share profit on an agreed ratio. The condition is that, if the enterprise goes into loss, the monetary investor bears these losses, whereas the executioner simply receives no reward for his invested knowledge and time.
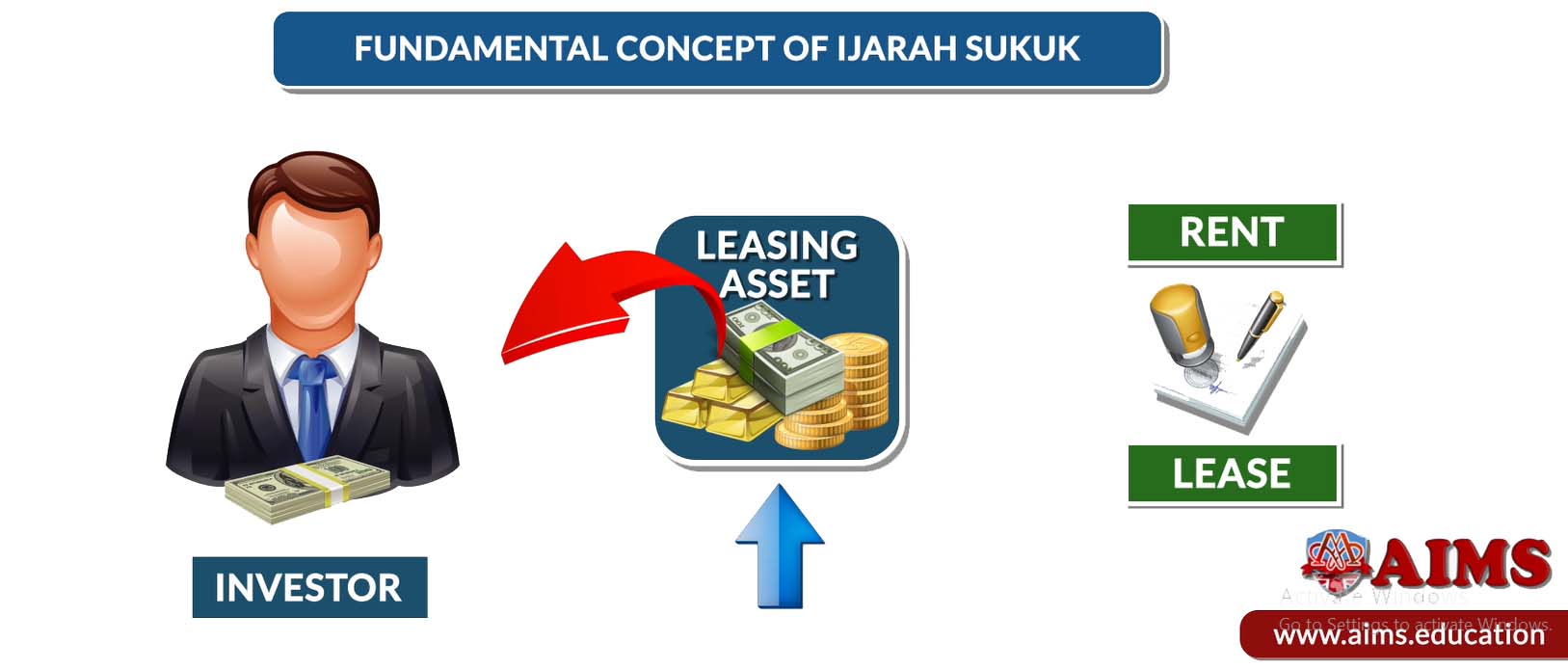
2. Ijarah Sukuk
They are based on the principles of an Ijarah (Islamic lease) contract. The fundamental concept of an Ijara Sukuk is that the owners of an asset are investors authorized to collect a fee in return for leasing that asset. In simple words, this is essentially a rental or lease contract granting the right to use an asset in return for payment.
3. Partnership Sukuk
The partnership sukuk the kind of sukuk based on market system that is incompliance with the Islamic principles of Shirkah or partnership.
4. Ordinary Stocks
Same as common stocks or shares which represent the basic voting shares within a company or corporation. However, there are certain Shariah rules for investing in stocks. The holder of an ordinary Shariah complaint share is usually entitled to one vote per share, like a conventional counterpart. Through the system of ordinary stocks, equal ownership is made apparent with the system of distributing shares in accordance with the shareholder’s percentage ownership in the Shariah-compliant company.
5. Preferred Stocks
Everything other than the aforementioned shares of a company’s stock are, by definition, preferred stocks or shares.
6. Islamic Mutual Funds
Islamic mutual funds are investment vehicles consisting of funds collected by many investors for investment in Shariah-compliant securities such as stocks, bonds, money market instruments, and other such assets. Professional money managers are hired to handle these funds and allocate the fund’s investments with the intention of generating income for the fund’s investors.
7. Single Stock Futures
Contracts between two investors where a buyer agrees to pay a specified price for numerous shares of one stock at a scheduled time in the future. In this system, the seller’s duty is to deliver the stock at a decided price at the future day point, and all transactions must be made in accordance with the Muslim Laws and Sources of Shariah.
8. Islamic Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
These are investment vehicles that own, operate, or finance on real estate, in line with Islamic principles. The Malaysian REIT in the past and now UAE REIT markets are well-known for their Shariah-compliant real-estate investment options.
9. Islamic Derivatives
These contracts derive their value from the performance of an underlying entity, and they strictly follow Islamic principles of finance, which forbid Gharar (known as uncertainty), Maysir (known as gambling or speculation), and interest or Riba (see types of Riba for details).
Educational Opportunities to Develop Expertise in the Islamic Capital Market
- Centre for education in Islamic finance is crucial for professionals wishing to excel in the growing field of Islamic banking and finance.
- Various programs are available, including the Certified Islamic Banker program, which provides a comprehensive understanding of Islamic banking operations.
- For those seeking advanced knowledge, a post-graduate diploma in Islamic finance can enhance their understanding of Shariah-compliant financial services.
- For individuals interested in contributing to the higher academic sphere, a research-based doctorate in Islamic finance can offer an opportunity to explore uncharted terrains in the field.
AIMS’ Islamic finance programs not only provide theoretical knowledge but also equip students with the practical skills necessary to contribute to the Islamic capital market effectively.

Key Players in the Islamic Capital Market
The Islamic Capital Market is a vast and complex system that comprises various players, including issuers, investors, intermediaries, and regulators.
- Issuers are entities that require capital to finance their operations, such as corporations, governments, and financial institutions.
- Investors are individuals or institutions that provide capital to the issuers in exchange for a return.
- Intermediaries facilitate transactions between issuers and investors in the Islamic Capital Market. They include Islamic investment banks, Islamic asset management firms, and Islamic brokerage firms.
- Regulators are responsible to ensure that the market operates under Shariah principles for Islamic finance.
Challenges and Risks Associated With Islamic Capital Market:
Despite its many benefits, Islamic Captial Market also presents several challenges, such as:
- Lack of standardization in the Islamic financial market, unlike conventional banking and finance. Here are details on Islamic VS Conventional banking systems.
- Lack of liquidity, because many Islamic financial products, such as Sukuk, are illiquid and cannot be traded on secondary markets.
- Several type of Islamic financial risks are associated with the Islamic Captial Market, such as credit risk, market risk, and Shariah compliance risk.
Islamic Capital Market and the Global Economy
The Islamic Capital Market is an important component of the global economy, with a total value of over $4.6 trillion. The market is particularly significant in the Middle East and Southeast Asia, where Islamic finance has gained widespread acceptance. The growth of the ICM has also led to an increase in cross-border transactions, with issuers and investors from different countries and regions participating in the market.
It also has the potential to contribute to the development of the global Islamic economy by providing an alternative source of financing for infrastructure projects, such as airports, ports, and highways. This is particularly relevant in emerging markets, where governments may be unable to access traditional sources of financing.

Future of the Islamic Capital Market
- Islamic Capital Market is expected to continue growing in the future, as more issuers and investors seek to access the market. The market is also expected to become more standardized with the development of universal standards and practices. This will increase transparency and investor confidence in the market.
- The growth of the Islamic Capital Market is also expected to lead to an increase in cross-border transactions, with issuers and investors from different countries and regions participating.
Final Words
Just like the aforementioned, other elements of the Islamic capital market are also gradually coming into prominence, along with the growth of Islamic trade finance. The already massive global economy is expanding by the day. Abandoning tradition, however, is not a necessity to partake in this worldwide culture of progress. The Islamic capital market products are a prime example of a system that integrates values of Islam and that of modernity and progress simultaneously.
